19th Dynasty Collection (page 8)
The 19th Dynasty of ancient Egypt, which spanned from the 13th to the 12th century BC, was a period marked by significant cultural and artistic achievements
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
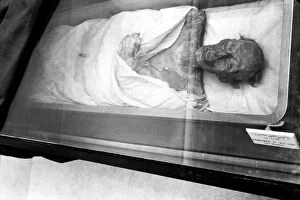
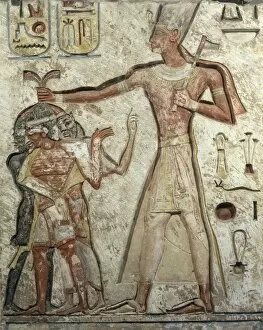
The 19th Dynasty of ancient Egypt, which spanned from the 13th to the 12th century BC, was a period marked by significant cultural and artistic achievements. The Book of the Dead of Hunefer, dating back to around 1450 BC, provides us with valuable insights into the religious beliefs and rituals of this era. One captivating fresco from the tomb of Queen Nefertari in Thebes depicts her engaged in a game of chess, showcasing not only her intelligence but also highlighting recreational activities enjoyed by royalty during that time. Another fascinating artwork is "The Fumigation of Osiris" found in the Book of the Dead belonging to Neb-Qued. This piece showcases intricate details and symbolism related to death and rebirth. Intriguingly, Goddess Hathor is depicted offering her necklace to Pharaoh Seth I in a painted relief from his tomb at Thebes. This gesture symbolizes divine protection bestowed upon him as indicated by Seth's cartouche. Statuary groups representing Pharaoh Ramesses II and his wife Nefertari provide us with glimpses into their royal lives. These sculptures showcase their regal attire and serve as a testament to their power and status within society. Moving on to Queen Nefertari's tomb in Luxor's Valley of Queens, detailed frescoes adorn its burial chamber walls. One particular scene shows Queen Nefertari being preceded by Isis, emphasizing her connection with this powerful goddess. Rameses II himself is immortalized through various artworks such as an artistically rendered portrait created by Winifred Mabel Brunton in 1926. His reign left an indelible mark on Egyptian history due to his military conquests and architectural endeavors like Abu Simbel temple complex. Egyptian wall paintings depicting Nefertari alongside Isis further emphasize the significance placed on these deities during this dynasty. Their presence highlights both religious and political aspects of ancient Egyptian society.