Acid Collection (#10)
"Exploring the Effects of Acid: From Porthgain Lime Workings to Chemistry Laboratories" The Porthgain lime workings in Pembrokeshire, West Wales
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
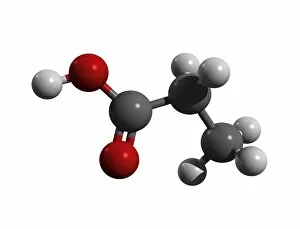
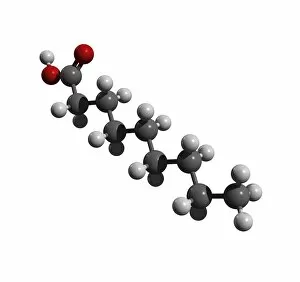
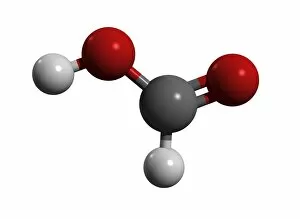
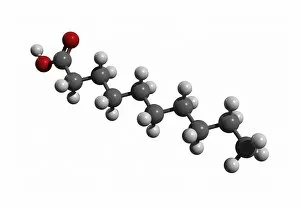
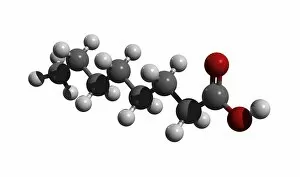
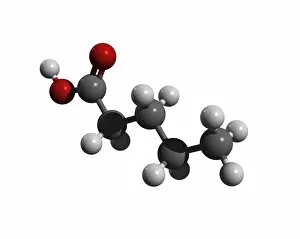
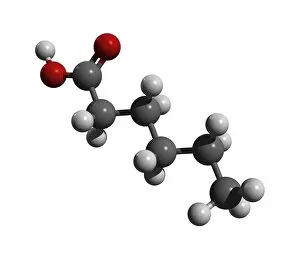
"Exploring the Effects of Acid: From Porthgain Lime Workings to Chemistry Laboratories" The Porthgain lime workings in Pembrokeshire, West Wales, stand as a testament to the historical significance in extracting limestone for various purposes. A slice of Canyon Diablo meteorite reveals the powerful impact that they can have on celestial bodies, shaping their composition and structure over millions of years. Rust treatment is just one example of how they can be harnessed for practical applications, preserving and restoring metal surfaces with their corrosive properties. The creatine amino acid molecule showcases the intricate nature of organic compounds influenced by acids, playing a crucial role in muscle function and energy production. Unveiling an unexpected connection between suffragette history and acid, militant attacks on golf courses during protests shed light on unconventional methods employed by activists fighting for women's rights. Acid rain has deeply eroded the limestone pavement above Malham Cove, leaving behind clints (lumps) and grykes (gaps), which provide unique habitats for rare plants like hart's tongue ferns. Forestry workers utilizing forwarder machines demonstrate how acid-free environments are essential when removing felled timber from Dunwich Forest to preserve its natural balance. The Murchison CM2 carbonaceous chondrite meteorite holds valuable insights into our understanding of early solar system chemistry and the role that acids played in its formation. Stepping back in time to 19th-century chemistry laboratories unveils vintage equipment used to study acids' properties - a testament to humanity's continuous exploration into this fascinating realm. Victoria College's Alexandria Chemistry Laboratory stands as a hub where young minds delve into experiments involving various types of acids, fostering scientific curiosity among future chemists. "From Cellar to Bar" captures the transformative power of acidic fermentation processes involved in brewing and winemaking, where sugars are converted into alcohol, creating delightful beverages.