Ammeter Collection
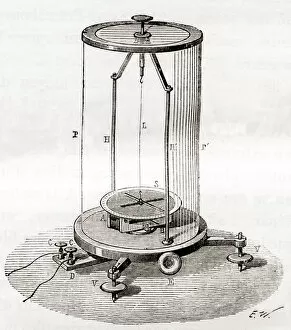
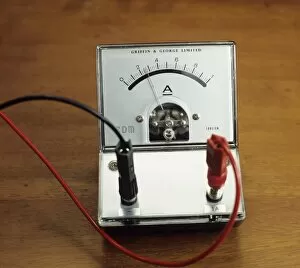
An ammeter, an early galvanometer and a type of measuring instrument used to measure electricity in therapeutics
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
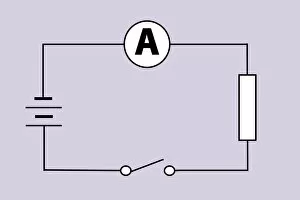
An ammeter, an early galvanometer and a type of measuring instrument used to measure electricity in therapeutics. This captivating black and white photo showcases William Edward Ayrton, a renowned British physicist, electrical engineer, and inventor in 1892. Another image from around the same time period features Ayrton himself with his invention. An illustration of the it is included, giving us a glimpse into its design. The ammeter's versatility is demonstrated through various experiments such as resistance tests using batteries, resistors, and the ammeter itself. In one experiment, electromagnetism's effect on a compass needle is shown by utilizing the battery, variable resistor, compass, wires along with the trusty ammeter. Ohm's Law comes alive in an electrical circuit diagram featuring both an ammeter and voltmeter; here we see how thin wires can impede current flow due to their resistance. Furthermore, this device proves useful even when connected to lightbulbs for measurement purposes. From different angles like front view or within a multimeter setup - the ever-reliable ammeter continues to play its role efficiently in understanding and analyzing electric currents.