Atome Collection
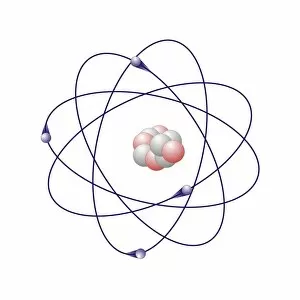
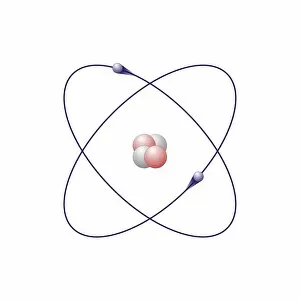
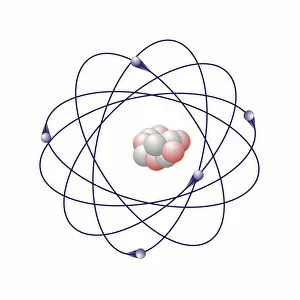
Atome: Unveiling the Intricacies of Atomic Models and Molecules Delving into the world of atoms, we encounter Beryllium
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
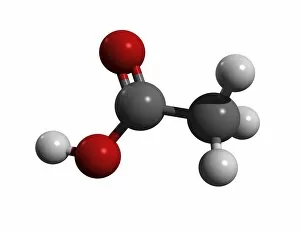
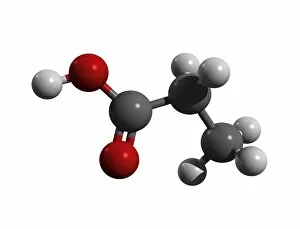
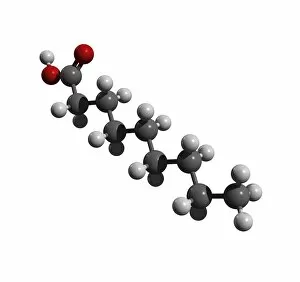
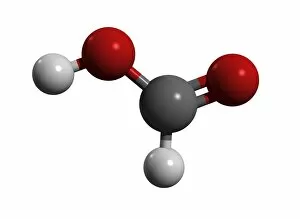
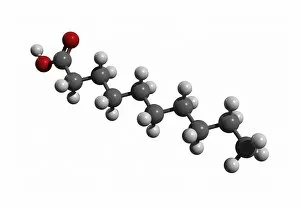
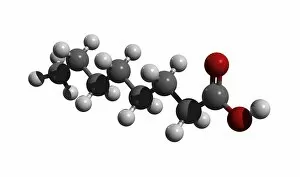
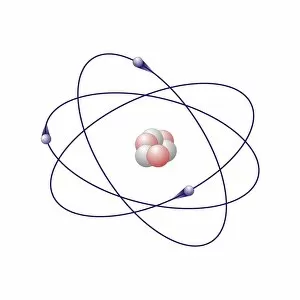
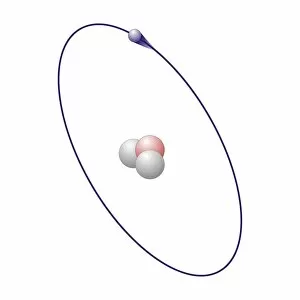
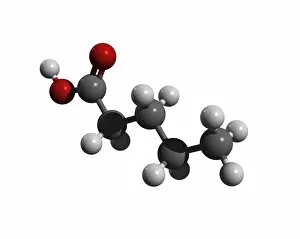
Atome: Unveiling the Intricacies of Atomic Models and Molecules Delving into the world of atoms, we encounter Beryllium, a fascinating element with an intricate atomic model. Its four electrons orbiting around its nucleus paint a mesmerizing picture of atomic structure. Moving on to Helium, another captivating element with its own unique atomic model. With two electrons gracefully circling its nucleus, it showcases simplicity in design yet holds immense importance in various scientific applications. Boron enters the stage next, showcasing its distinctive atomic model. This element's five electrons dance around its nucleus, forming an intriguing pattern that scientists have long studied and admired. Shifting our focus to molecules now, let us explore the wonders of propanoic acid. Its molecular structure captivates chemists worldwide as they unravel its composition and potential uses in different industries. Acetic acid follows suit; this molecule's arrangement intrigues researchers due to its role in vinegar production and various chemical processes that rely on it. Pelargonic acid takes center stage with an elaborate molecular structure that sparks curiosity among scientists who study fatty acids' properties and their significance in biological systems. Formic acid joins the ensemble; this molecule's compact yet powerful configuration makes it a vital component for many industrial applications such as preservatives or disinfectants. Captivating our attention next is capric acid - a compound found abundantly in coconut oil. Its complex molecular arrangement contributes to both cosmetic products and dietary supplements alike. The spotlight then shifts towards caprylic acid - known for being present in palm oil and milk fat. Scientists are intrigued by this molecule's versatile nature which finds application across several fields including medicine and food science research. Once again gracing us with their presence is capric acid - renowned for playing a crucial role as one of coconut oil's main components. This molecule continues to fascinate researchers exploring natural remedies or sustainable alternatives within the beauty industry. Concluding our molecular journey, we encounter butyric acid.