Aufbau Collection
Aufbau is a concept in chemistry that refers to the building up of atomic models and molecules
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
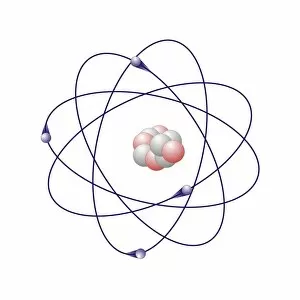
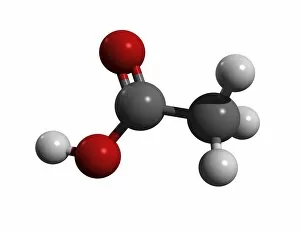
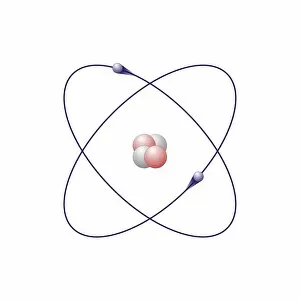
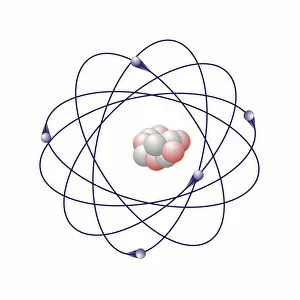
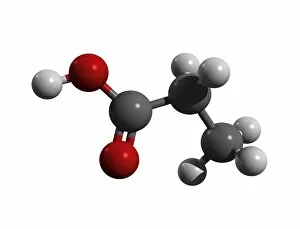
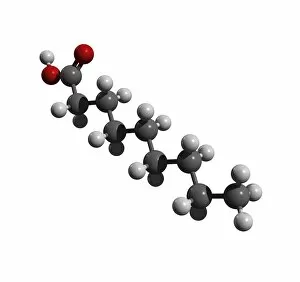
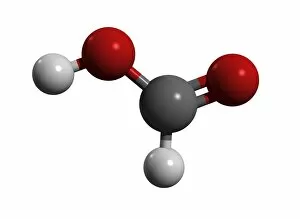
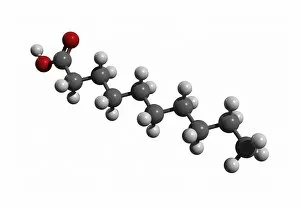
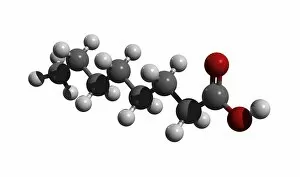
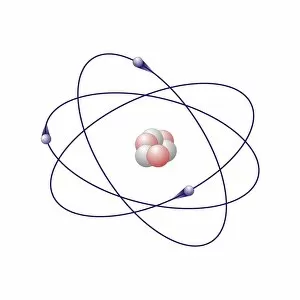
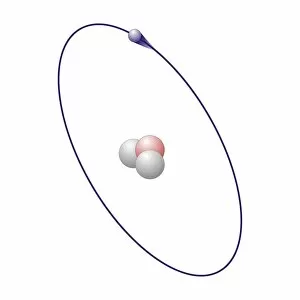
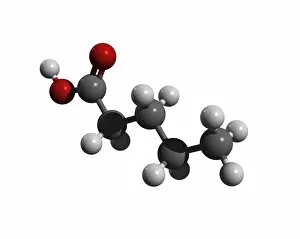
Aufbau is a concept in chemistry that refers to the building up of atomic models and molecules. It involves understanding the arrangement of electrons within an atom or molecule, which determines its chemical properties. One example is seen in Beryllium's atomic model. With four electrons, it follows the pattern of filling orbitals from lowest to highest energy levels. Similarly, Helium's atomic model demonstrates aufbau as it fills its first energy level with two electrons. Moving on to molecules, Propanoic acid showcases aufbau by arranging its atoms - carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen - in a specific order to form a stable structure. Acetic acid also exemplifies aufbau through its molecular composition of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms bonded together. Pelargonic acid displays aufbau by organizing carbon and hydrogen atoms into a long chain structure with a carboxyl group at one end. Formic acid exhibits aufbau as it arranges carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms into a simple yet crucial molecule found naturally in various organisms. Capric acid follows the principles by constructing itself using carbon and hydrogen atoms arranged in a specific way for stability. Caprylic acid shares similarities with capric acid regarding their molecular structures based on the principles but differs slightly due to variations in their arrangements. Butyric acid demonstrates how different combinations of carbon and hydrogen can create distinct molecules following the rules set forth by aufbau theory. Lastly, Lithium's atomic model adheres to aufbau principles as it fills electron shells according to increasing energy levels within an atom.