Cancer Cell Collection
"Cancer Cell: Unveiling the Intricacies of a Silent Menace" In the realm of medical research, HeLa cells have emerged as an invaluable tool for scientists
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
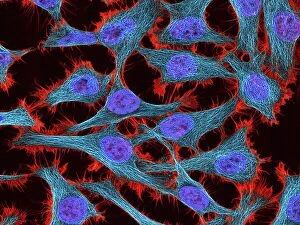
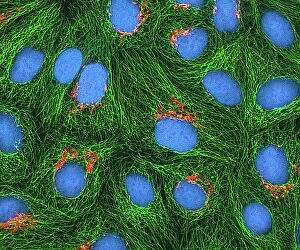
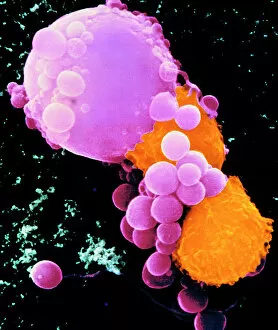
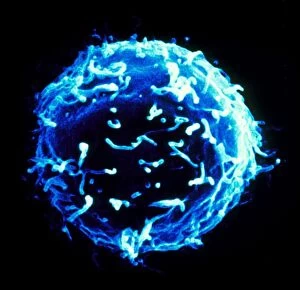
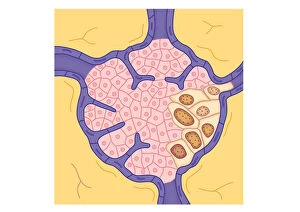
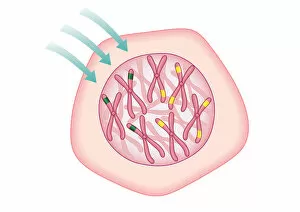
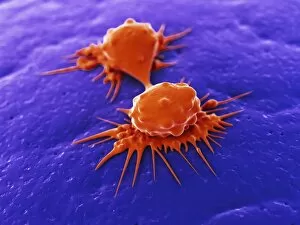
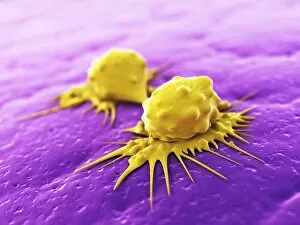
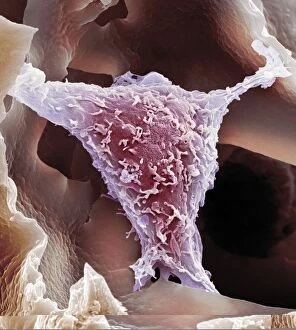
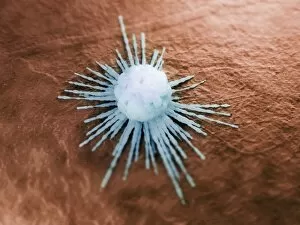
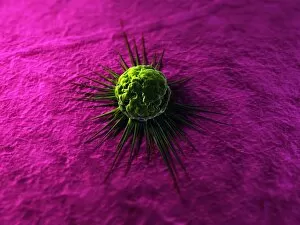
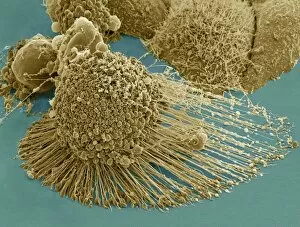
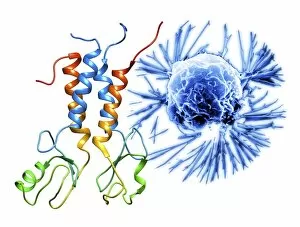
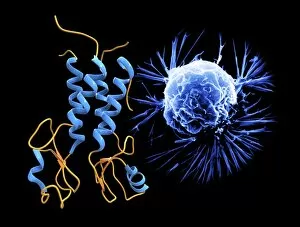
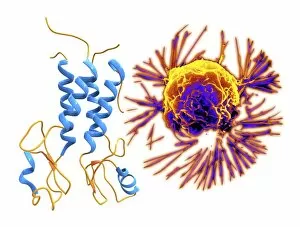
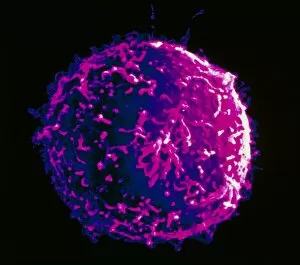
"Cancer Cell: Unveiling the Intricacies of a Silent Menace" In the realm of medical research, HeLa cells have emerged as an invaluable tool for scientists. Captured in light micrographs C017/8299 and C017/8298, these immortal cells derived from Henrietta Lacks continue to unravel the mysteries of cancer. A colored scanning electron microscope (SEM) image showcases lymphocytes valiantly attacking a cancer cell, highlighting our immune system's relentless battle against this disease. Similarly, another SEM image reveals a leukaemic white blood cell M132/0488, emphasizing the urgency to find effective treatments for leukemia. Through digital illustrations, we witness how cancerous cells divide and lodge themselves within narrow blood vessels and surrounding tissues – forming secondary tumors that pose great danger. Furthermore, breached lymph vessels allow primary tumors to invade adjacent tissues while tumor growth within lymph nodes becomes evident through vivid visuals. The destructive nature of cancer is further depicted as digital illustrations showcase blood vessel walls rupturing under pressure from expanding primary tumors. This rupture enables detached cancerous cells to spread throughout the body via blood flow – a harrowing process known as metastasis. Additionally, temporary damage caused by carcinogens attacking genes on chromosomes is illustrated digitally - shedding light on one possible cause behind genetic mutations leading to malignancy. To comprehend the intricate structure of tumor-forming cancer cells at different stages, cross-sectional biomedical illustrations are presented. These images reveal their progressive growth during first and second doubling stages - providing crucial insights into potential intervention points along this deadly journey. As we delve deeper into understanding these complex mechanisms underlying cancer progression, researchers strive tirelessly towards breakthroughs that will ultimately lead us closer to effective prevention strategies and life-saving treatments.