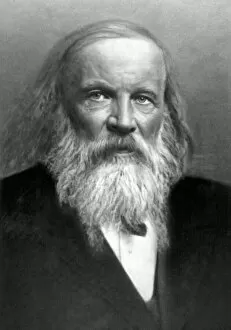Chemical Elements Collection
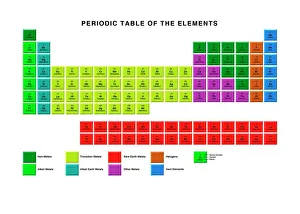
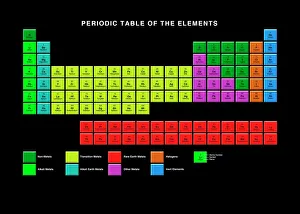
Chemical Elements: Unveiling the Building Blocks of Matter In 1869, Dmitry Mendeleyev, a brilliant Russian chemist
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
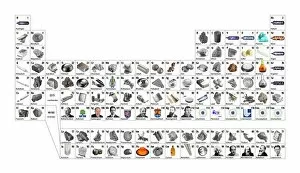
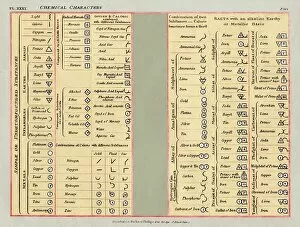
Chemical Elements: Unveiling the Building Blocks of Matter In 1869, Dmitry Mendeleyev, a brilliant Russian chemist, introduced his groundbreaking creation to the scientific world—the Mendeleyev's periodic table. This remarkable invention revolutionized our understanding and their properties. The standard periodic table we know today owes its existence to Mendeleyev's visionary work. It organizes elements into groups based on their atomic number and similar characteristics. From metals to non-metals, transition metals to noble gases, this comprehensive chart encompasses all known element types. Meticulously engraved by George J. Stodart, an exquisite portrait immortalizes Dmitri Mendeleev himself—a tribute to his immense contributions in unraveling the secrets of matter. Alongside him stands John Dalton, a British chemist who laid the foundation for modern atomic theory. Ramsay's discharge tubes for noble gases stand as testament to William Ramsay's pioneering experiments with these elusive elements that resist bonding with other substances. These glass tubes allowed scientists to observe their unique spectral colors and understand more about their behavior. Robert Boyle, an Anglo-Irish chemist from centuries past also finds his place among these luminaries who shaped our knowledge of chemical elements. His meticulous observations paved the way for future discoveries in chemistry. Collaboration is key in scientific progress; thus Bohuslav Brauner joins forces with Dmitri Mendeleev in exploring new frontiers within this realm. Together they delve deeper into understanding elemental properties and expanding upon Mendeleyev’s original masterpiece. A pictorial periodic table captures attention through visual representation—colorful blocks representing each element adorn this artistic rendition of scientific knowledge. It serves as a reminder that science can be both informative and aesthetically captivating. Chemical symbols are like secret codes revealing the identity of each element at a glance—H for hydrogen or Au for gold—they provide concise information about an element's atomic structure and properties.