Chemical Synapses Collection
Chemical synapses play a crucial role in the intricate network of communication within our brain
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
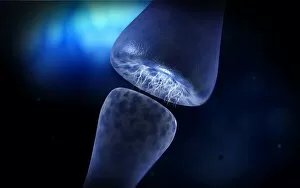
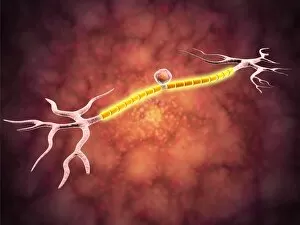
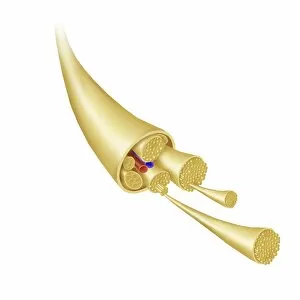
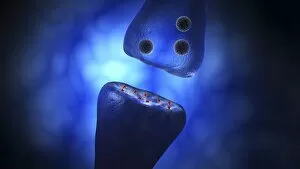
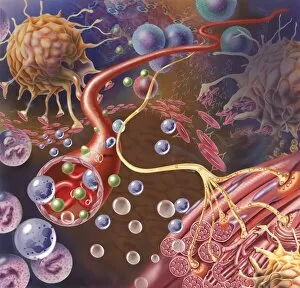
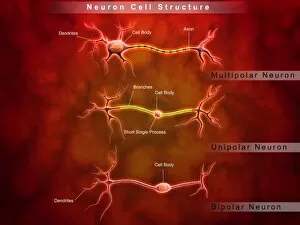
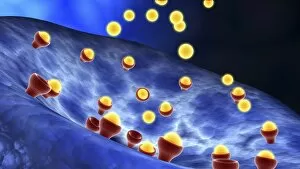
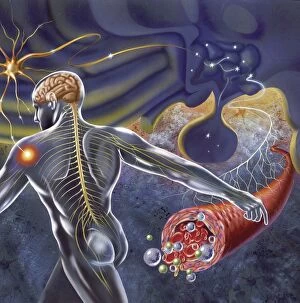
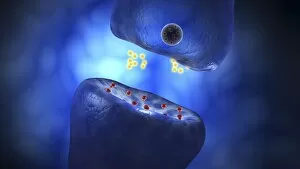
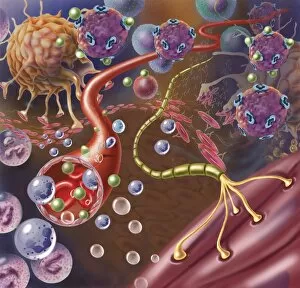
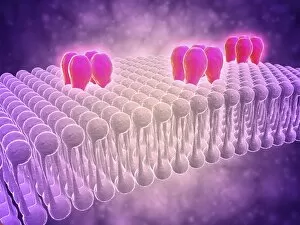
Chemical synapses play a crucial role in the intricate network of communication within our brain. This conceptual image of a synapse inside the brain showcases the remarkable complexity and interconnectedness of neurons. Zooming in, we observe a microscopic view revealing multiple nerve cells, known as neurons, which are fundamental units responsible for transmitting information throughout our nervous system. One such neuron captured here is an unipolar neuron, highlighting its unique structure. The detail of a nerve bundle reminds us that these synapses exist not only individually but also form extensive networks that enable efficient transmission of signals across different regions of the brain. Synaptic vesicles, depicted conceptually in another image, contain neurotransmitters - chemical messengers essential for communication between neurons. These vesicles release their contents into the synaptic cleft during neurotransmission. In this captivating conceptual image depicting a human brain with neurons firing away, we witness the dynamic nature and constant activity within our brains. Each firing neuron contributes to various cognitive processes and behaviors. A closer look at one particular synapse reveals how it functions as a messenger station: transmitting pain messages from an injured muscle to be processed by our central nervous system. Another fascinating snapshot captures the moment when neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft during synaptic transmission. This process allows information to flow seamlessly from one neuron to another. Understanding the anatomy structure of neurons is vital in comprehending how chemical synapses operate efficiently. Their complex dendritic branches receive incoming signals while axons transmit outgoing signals to other neurons or target tissues. Conceptual images showcasing synapse receptors emphasize their critical role in receiving neurotransmitters and initiating further signaling pathways within postsynaptic neurons or effector organs. Lastly, this schematic illustrates how nerve impulses originating from various parts of our body reach important control centers like the hypothalamus through chemical synapses. These impulses trigger appropriate responses necessary for maintaining homeostasis and regulating bodily functions effectively.