Chemie Collection
"Exploring the Fascinating World of Chemie: From Fruit-Powered Clocks to Atomic Models and Molecules" Chemie, the captivating realm of chemistry
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
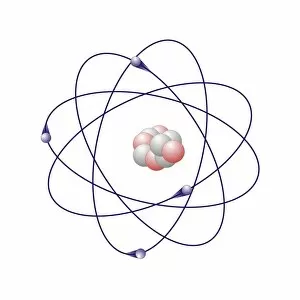
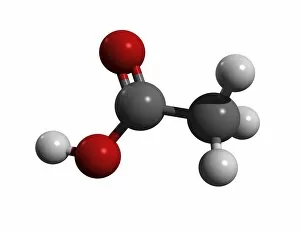
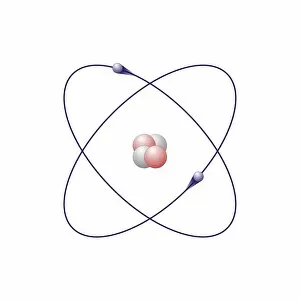
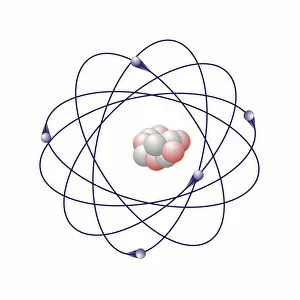
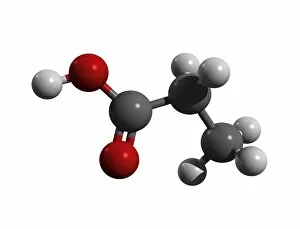
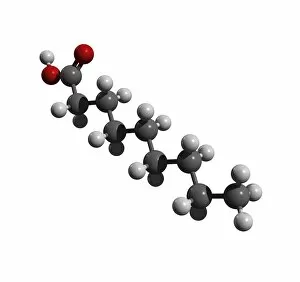
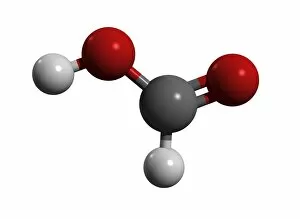
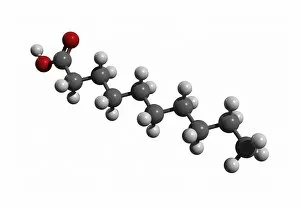
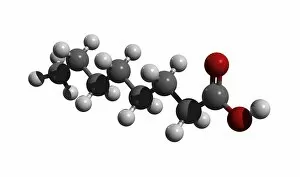
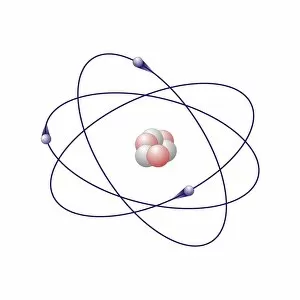
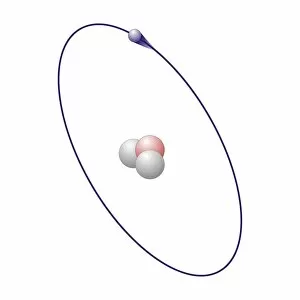
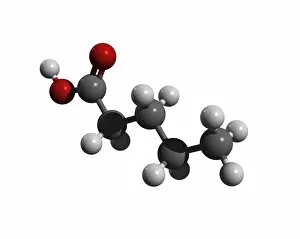
"Exploring the Fascinating World of Chemie: From Fruit-Powered Clocks to Atomic Models and Molecules" Chemie, the captivating realm of chemistry, unveils a myriad of wonders that shape our understanding of the world. Delve into this enchanting domain as we embark on a journey through various intriguing aspects. Ever wondered how fruit can power a clock? Enter the realm and witness the magic unfold before your eyes. Through chemical reactions, fruits generate electricity that can be harnessed to power timepieces – an astonishing fusion of nature and science. Beryllium, Helium, Boron – these atomic models hold secrets waiting to be unraveled. Peer into their intricate structures and marvel at their unique properties. These elements form the building blocks upon which countless phenomena in our universe are based. Molecules play a crucial role in chemie's tapestry. Propanoic acid molecule, Acetic acid molecule, Pelargonic acid molecule, Formic acid molecule - each with its distinct composition and characteristics. Explore their intricacies as they contribute to diverse fields such as medicine or food industry applications. Capric acid molecule, Caprylic acid molecule - these compounds possess fascinating attributes that make them valuable for various purposes ranging from cosmetics to pharmaceuticals. Uncover their hidden potential within chemie's vast repertoire. Butyric acid molecules offer yet another intriguing facet within this captivating discipline. Their distinctive aroma contributes to flavors found in dairy products like butter or cheese while also playing essential roles in other industries such as perfumery or even biofuel production. As we unravel the mysteries concealed within chemie's depths, one thing becomes evident: it is an ever-evolving field brimming with endless possibilities for exploration and innovation. Whether it's unlocking nature's secrets or harnessing chemicals' transformative powers for practical use – chemie continues to captivate minds worldwide.