Coagulation Collection
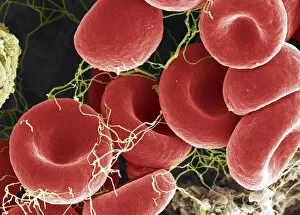
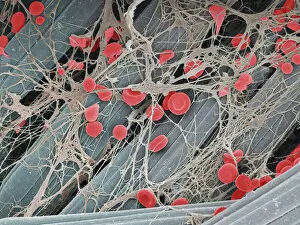
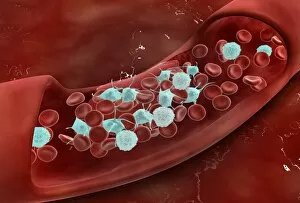
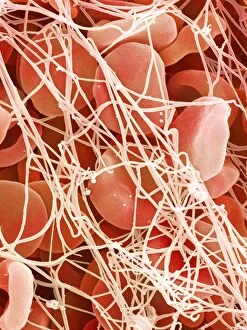
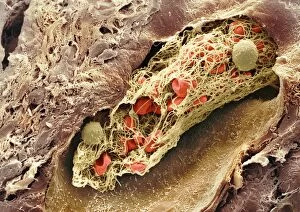
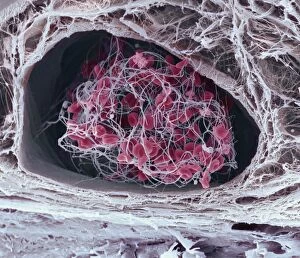
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Coagulation: From Blood Clots to Arterial Plaque" Witness the intricate process as a blood clot forms on a plaster, captured under SEM
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
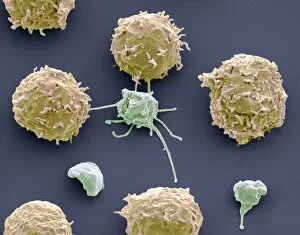
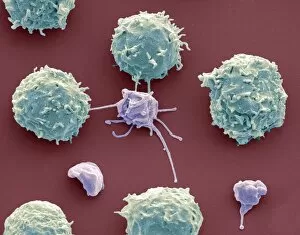
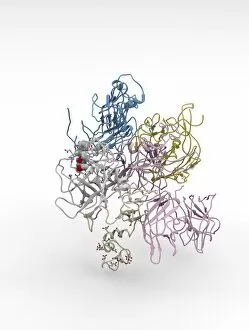
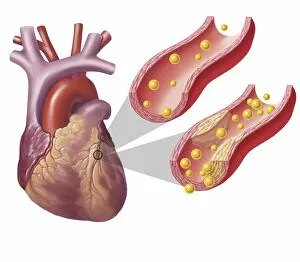
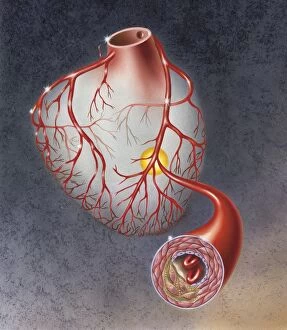
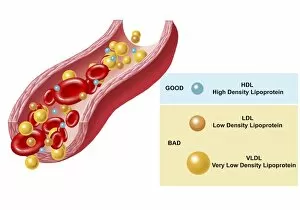
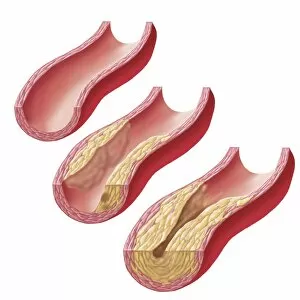
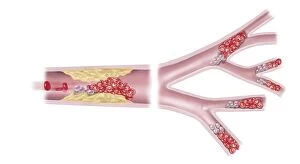
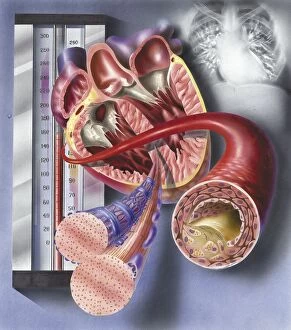
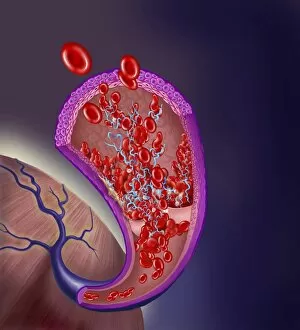
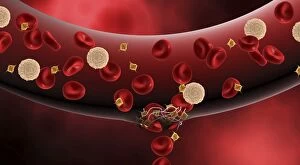
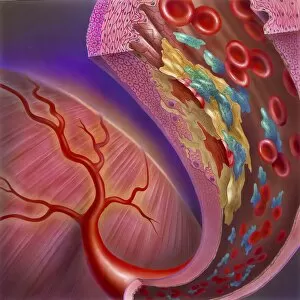
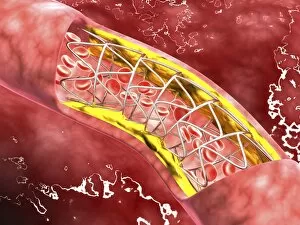
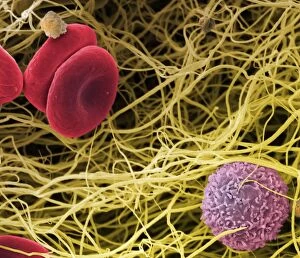
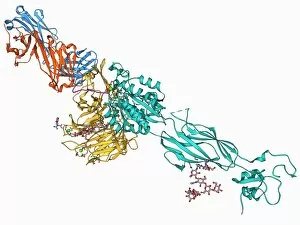
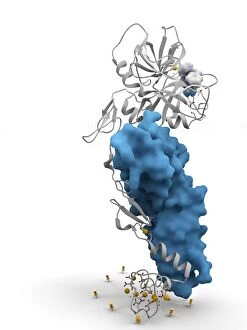
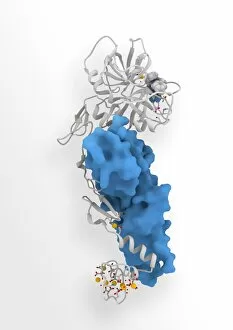
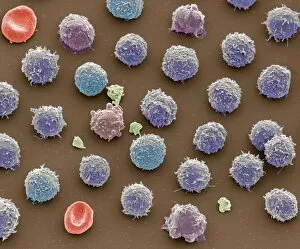
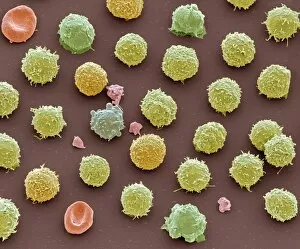
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Coagulation: From Blood Clots to Arterial Plaque" Witness the intricate process as a blood clot forms on a plaster, captured under SEM. Delve into the microscopic world and explore white blood cells and platelets in action, as seen through SEM C016 / 3099. Marvel at the dynamic interplay between white blood cells and platelets within our bloodstream, revealed by SEM C016 / 3098. Unravel the complex molecular structure factor complexes with molecule C014 / 0139. Journey inside the heart's arteries to discover cholesterol accumulation in one artery while plaque builds up in another. Explore an arterial landscape marred by atherosclerotic plaque, offering insights into its detrimental effects on cardiovascular health. Peer through a microscope lens to witness blood clotting taking place within an artery – a captivating sight that reveals nature's defense mechanism gone awry. Observe both good and bad cholesterol coursing through our bloodstream, playing pivotal roles in cardiovascular health management. Examine closely the gradual buildup of atherosclerotic plaque within an artery – an ominous sign demanding attention for preventive measures against heart disease. Gain insight into acute coronary syndrome with microvascular obstruction – shedding light on potential complications arising from impaired blood flow to vital cardiac tissues. Embark on an interior tour of the heart, where muscle cells intertwine with diseased arteries affected by atherosclerosis – highlighting its impact on overall cardiac function and wellbeing. Witness thrombus formation occurring on a valve nestled within a vein - unraveling yet another aspect of coagulation's influence. In this captivating journey through images capturing various aspects of coagulation, we gain valuable knowledge about its role in both protecting and endangering our cardiovascular health.