Cosmological Collection (#3)
Exploring the vastness of the cosmos, the Hubble Ultra Deep Field 2012 captures a mesmerizing glimpse into the celestial wonders that lie beyond
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
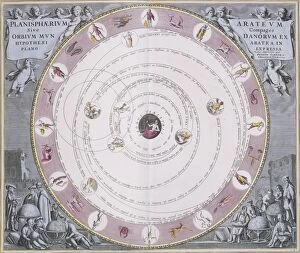
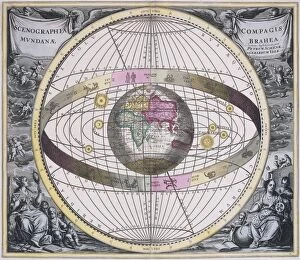
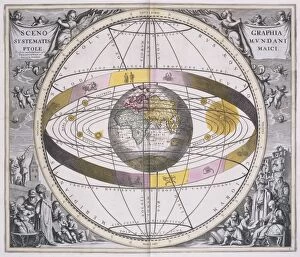
Exploring the vastness of the cosmos, the Hubble Ultra Deep Field 2012 captures a mesmerizing glimpse into the celestial wonders that lie beyond. Galaxies, like sparkling jewels scattered across the velvet canvas of space, reveal their intricate dance through celestial mechanics. Akin to medieval artwork depicting cosmic mysteries, these galaxies hold secrets waiting to be unraveled. In a collision of protons in C014 / 1797, scientists at CERN's ATLAS detector delve deeper into understanding our universe's building blocks. The enigmatic Cosmic Microwave Background whispers tales from its birth during the Catalan Atlas in the 14th century. As we trace our origins back to this ancient relic, we marvel at how far we have come. The Milky Way stretches across billions of light-years, an ethereal river guiding us through time and space. Conceptual artwork visualizes elusive particles like the Higgs boson detected by CMS detector at CERN - unlocking new dimensions within our understanding. Gazing upon Jupiter from Europa's icy surface transports us to otherworldly realms where imagination meets reality. Artistic renderings bring alive a Universe timeline - showcasing milestones etched throughout eternity. Cosmological hints beckon us towards infinite possibilities as we continue on this awe-inspiring journey of exploration and discovery.