Crystalline Collection (#12)
"Captivating Crystalline Beauty
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
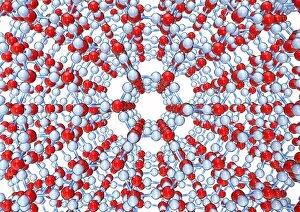
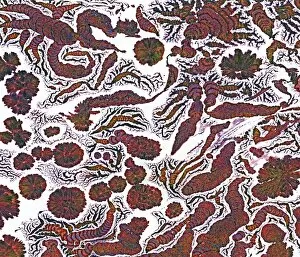
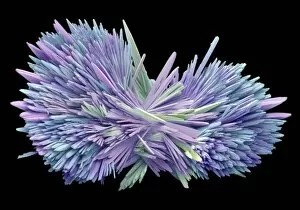
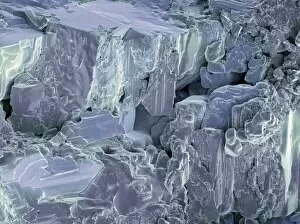
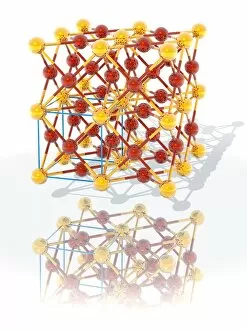
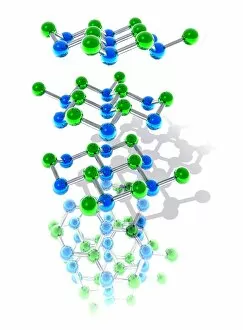
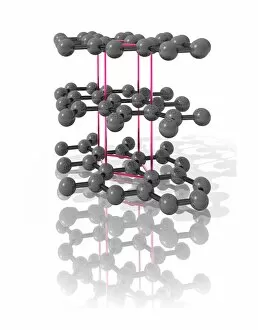
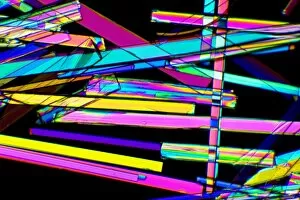
"Captivating Crystalline Beauty: A Glimpse into the Intricate World of Minerals and Molecules" Delicate copper and magnesium sulphate crystals under a powerful light microscope (LM) reveal their mesmerizing structure. Caffeine crystals, captured in a stunning light micrograph, showcase the intricate patterns formed by this stimulating compound. The perovskite crystal structure unveils its remarkable symmetry, creating an enchanting visual spectacle. A computer artwork depicts the brilliance of a diamond's crystalline lattice, reflecting its timeless allure. Cortisol crystals, magnified through a light micrograph (LM), exhibit their unique formation within our body's natural stress hormone. Vibrant copper sulphate crystals come to life when observed under a high-resolution light microscope (LM), revealing their captivating hues and shapes. The beach of Capo Coda Cavallo in Sardinia, Italy offers breathtaking views where nature's crystalline beauty meets pristine shores - truly an idyllic escape in Europe. Another glimpse into caffeine's microscopic world showcases its delicate crystal formations through an exquisite light micrograph. An artistic representation reveals the intricate patterns found within graphene sheets - highlighting both scientific marvels and aesthetic wonders. Baking soda crystals take on extraordinary shapes when examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), unveiling hidden textures that captivate the eye. Copper sulphate crystals shimmer with elegance as they are unveiled through the lens of a high-resolution light microscope (LM). A fly delicately perched on sugar granules is brought to life through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), showcasing how even everyday substances can possess unexpected beauty. In this collection of images and descriptions lies proof that there is unparalleled beauty hidden within every corner of our world – from minerals to molecules – reminding us to appreciate nature's artistry at both macroscopic and microscopic levels.