Cultured Collection (#4)
"Cultured: Exploring the Beauty and Complexity of Life's Artistry" Step into a world where art meets science, where beauty intertwines with knowledge
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
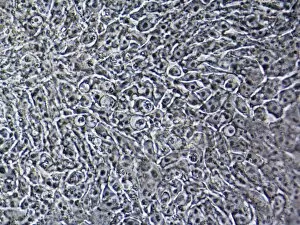
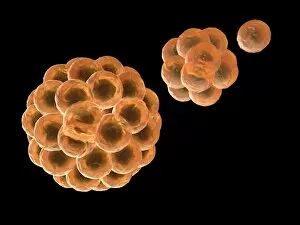
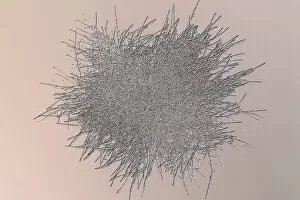
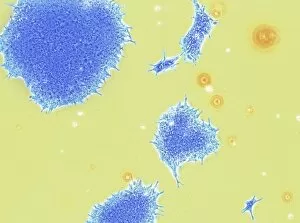
"Cultured: Exploring the Beauty and Complexity of Life's Artistry" Step into a world where art meets science, where beauty intertwines with knowledge. From ancient civilizations to modern breakthroughs, the concept of "cultured" takes on new meaning as we delve into the wonders of human creativity and scientific exploration. Intricate sculptures like the Bust of goddess Tanit transport us back to Carthaginian times, showcasing their mastery in capturing divine beauty through art. The attention to detail and craftsmanship displayed in these pieces is truly awe-inspiring. But our journey doesn't stop there; it delves deeper into the microscopic realm. Witnessing HeLa cells under a light micrograph reveals their intricate structures, reminding us that even at this minuscule level, life holds immense complexity and wonder. Glial stem cell cultures further highlight how different types of cells can be nurtured and grown in controlled environments for research purposes. Embryonic stem cells take center stage alongside a needle in an SEM image, symbolizing both hope for medical advancements and ethical debates surrounding their use. These versatile cells hold tremendous potential for regenerative medicine but also raise questions about ethics and boundaries. Neural stem cell cultures demonstrate our ability to cultivate specific types of brain cells outside their natural environment – a testament to humanity's relentless pursuit of understanding our own minds. Nerve cells captured through SEM imagery showcase their intricate branching patterns that enable communication within our nervous system. Venturing beyond human biology, we encounter Vesicular stomatitis virus under TEM – an insight into microbial worlds that shape our existence. Bacterial cultures remind us that life thrives not only within ourselves but also all around us – invisible yet impactful. Finally, plant biotechnology emerges as another facet expression. Through genetic engineering techniques, scientists have harnessed nature's potential by modifying plants' genetic makeup for various purposes such as increased crop yield or disease resistance.