Endometrial Collection
"Exploring the Intricacies of Endometrial Conditions: From Polyps to Cancer" Endometrial polyps, small growths within the uterus
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
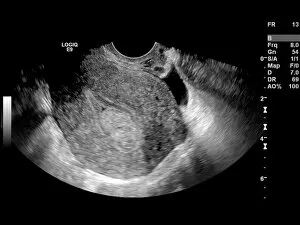
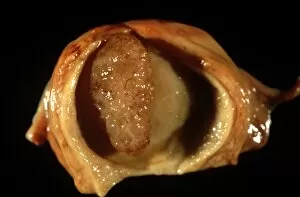
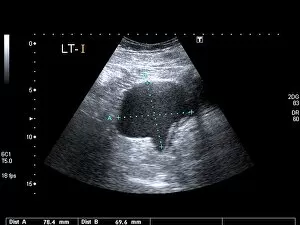
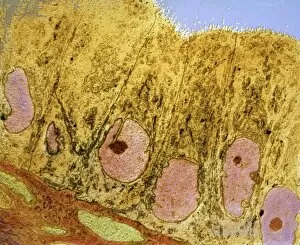
"Exploring the Intricacies of Endometrial Conditions: From Polyps to Cancer" Endometrial polyps, small growths within the uterus, captured in an ultrasound scan (C017 / 7800), revealing their presence and location. X-rays (C018 / 0587) provide a detailed view polyps, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning for patients. Another X-ray image (C018 / 0588) showcases the intricate nature polyps, emphasizing the need for accurate detection methods. Under a light microscope (C015 / 7104), endometrial hyperplasia is observed - an overgrowth of cells that can potentially lead to cancer if left untreated. A close-up shot (C015 / 6745) captures an individual endometrial polyp, highlighting its distinct features and potential impact on reproductive health. In another image (C015 / 6742), multiple endometrial polyps are visible within the uterine cavity, underscoring their prevalence among women worldwide. Through a light micrograph (C015 / 6061), we witness the cellular abnormalities associated with endometrial cancer - a serious condition requiring prompt medical attention. Secondary endometrial cancer is depicted in C015/6058; this image emphasizes how cancers from other parts of the body can spread to affect the uterine lining as well. An ultrasound scan reveals an endometrial cyst (C017 /8006); these fluid-filled sacs may cause discomfort or fertility issues if not managed appropriately by healthcare professionals. Continuing our exploration through ultrasound imaging (C017/7799), we observe another instance where an endometrial polyp is detected early on using non-invasive techniques. 11 &12.