Experimenting Collection (#6)
"Unleashing the Power of Curiosity: A Journey through Centuries of Experimentation" Embarking on a thrilling adventure, a man fearlessly rides atop a steam rocket
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
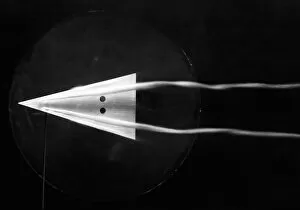
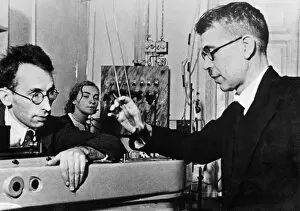
"Unleashing the Power of Curiosity: A Journey through Centuries of Experimentation" Embarking on a thrilling adventure, a man fearlessly rides atop a steam rocket, pushing the boundaries of human exploration. Meanwhile, in 1954, scientists utilize a mass spectrometer to unravel the mysteries hidden within matter. The revolutionary BAC TSR-2 takes flight, embodying the audacity and innovation that come with daring experiments. In the 1840s, Simpson delves into uncharted territories as he meticulously researches anaesthetics, forever changing medical practices. Pioneering minds like Sir Frank Whittle revolutionize aviation by inventing jet engines while Gregor Mendel's groundbreaking work as an Austrian botanist lays the foundation for our understanding of genetics. At Berkeley in 1955 C016 / 8832 marks an anti-proton experiment where scientists collide particles to unlock secrets about our universe. Antoine Lavoisier and his wife stand side by side in their laboratory - two brilliant chemists who redefine our knowledge of chemical reactions. A fruit-powered clock serves as a whimsical reminder that even everyday objects can become tools for experimentation. Witnessing particle collisions reveals glimpses into unseen dimensions and unravels nature's deepest secrets. An early telephone depicted in historical artwork reminds us how Alexander Graham Bell experimented relentlessly until he successfully transmitted sound over long distances. And who could forget Louis Pasteur? This French microbiologist pioneers pasteurization techniques that save countless lives from deadly diseases. From steam rockets to microscopic discoveries, it has been at the heart of human progress throughout history, and is through these bold endeavors that we push boundaries, challenge conventions, and pave new paths towards enlightenment and innovation.