False Colored Collection (#2)
"Unveiling Nature's Hidden Palette: Exploring the World Microscopy" Step into a mesmerizing realm where science and art converge
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
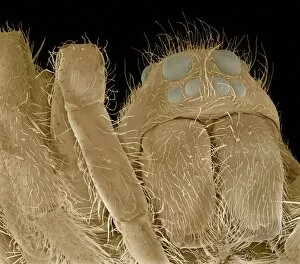
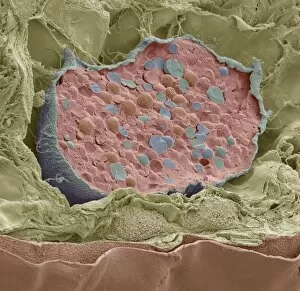
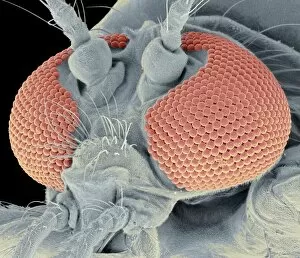
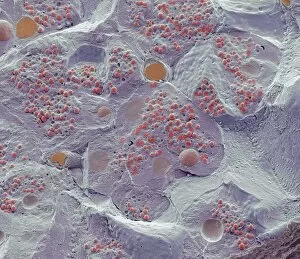
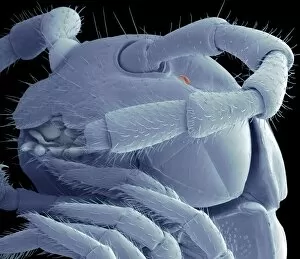
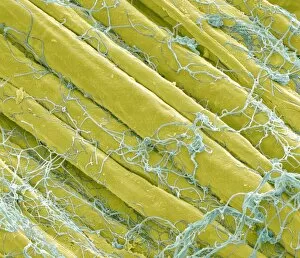
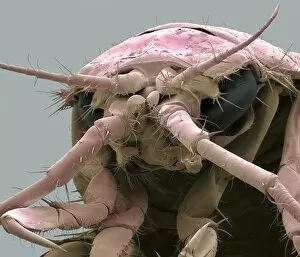
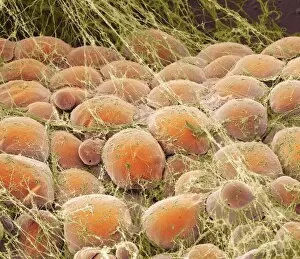
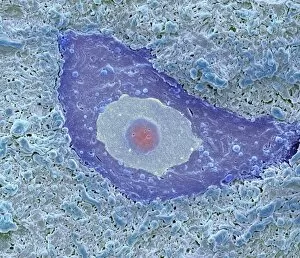
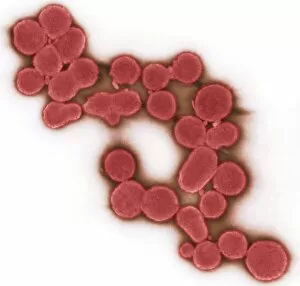
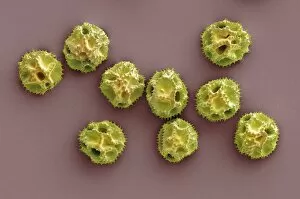
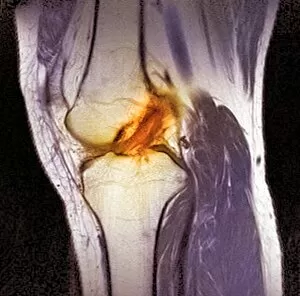
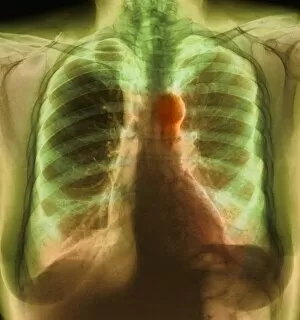
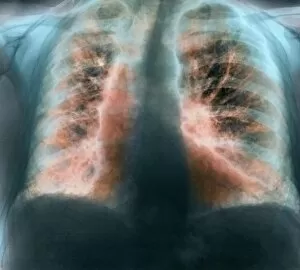
"Unveiling Nature's Hidden Palette: Exploring the World Microscopy" Step into a mesmerizing realm where science and art converge, revealing captivating details that are invisible to the naked eye. In this collection images captured through scanning electron microscopy (SEM), we embark on a journey through various specimens, each showcasing their unique beauty. First up, we encounter the intricate head of a honey bee, magnified to expose its delicate features in stunning hues. Moving on, we delve into the spiny world of a spider as its exoskeleton is brought to life with vibrant colors under SEM. Venturing deeper into nature's wonders, we explore the trachea lining - an enchanting network resembling an otherworldly landscape. Next, dandelion pollen grains take center stage; their textured surfaces transformed by false coloring techniques into an ethereal spectacle. As our exploration continues, Philadelphia fleabane pollen grains come alive in vivid shades against a dark backdrop. The gorse stigma adorned with pollen grains follows suit – an exquisite display reminiscent of abstract art. A surprising juxtaposition awaits as we discover a lily pollen grain delicately resting upon a rosemary leaf – contrasting textures and colors intertwining harmoniously. Meanwhile, the gorse flower bud reveals hidden secrets within its petals when observed at microscopic levels. Nature's diversity unfolds further with Forsythia pollen grains taking shape in brilliant tones that evoke feelings of warmth and vitality. Chickweed pollen grains add another layer to this symphony of color and form – tiny spheres bursting forth like miniature fireworks frozen in time. Intriguingly shifting gears from flora to fauna, human chromosomes emerge as striking patterns under SEM C013 / 5002 – reminding us how intricately woven our genetic makeup truly is. Finally, optic nerve fibers weave together like cosmic threads connecting our visual perception to reality itself. Through these false colored masterpieces created by scientific exploration, we are reminded of the hidden beauty that lies within our world.