Genetic Collection (page 8)
"Unlocking the Secrets: Exploring the Fascinating World of Genetics" In this captivating journey, we delve into the intricate realm of genetics
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
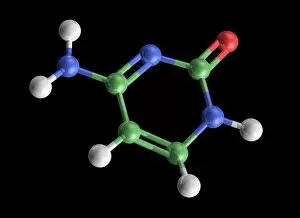
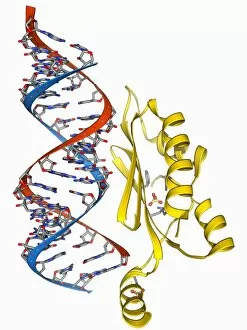
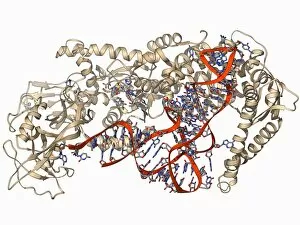
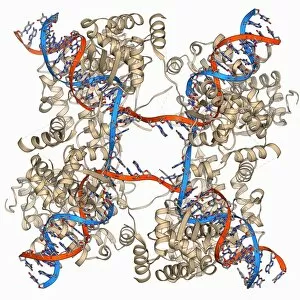
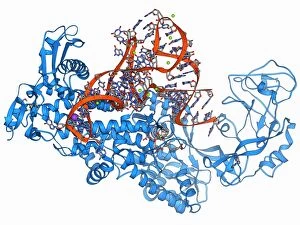
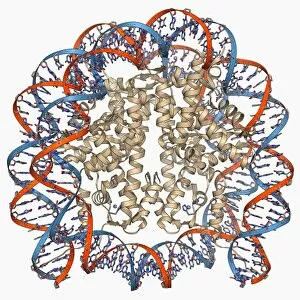
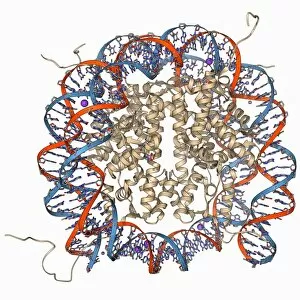
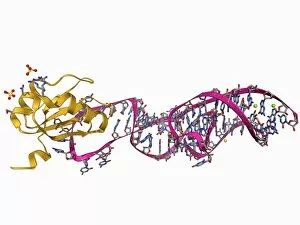
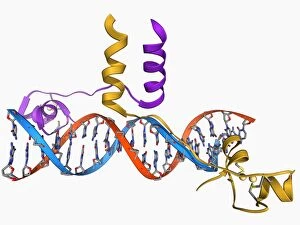
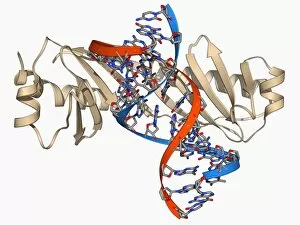
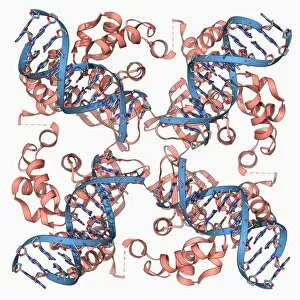
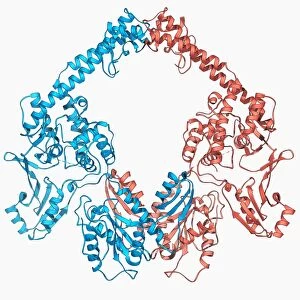
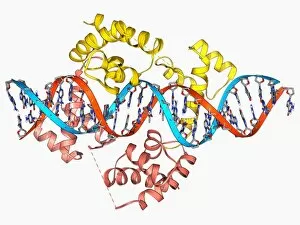
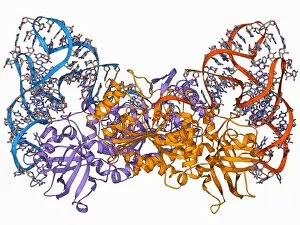
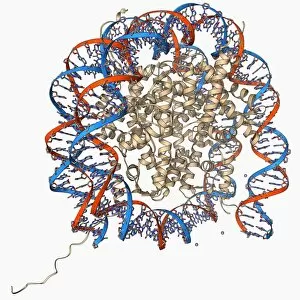
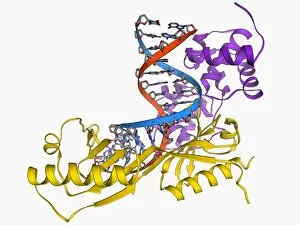
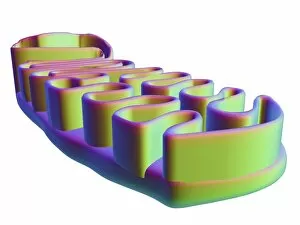
"Unlocking the Secrets: Exploring the Fascinating World of Genetics" In this captivating journey, we delve into the intricate realm of genetics, where computer screens display mesmerizing human genetic sequences. The double-stranded RNA molecule stands as a testament to the complex nature of our genetic makeup. Witness DNA transcription in action through a stunning molecular model, unraveling the process that shapes our very existence. Amidst this exploration, an elegant leopard in its melanistic phase rests gracefully on a log, reminding us of the diversity and beauty found within genes. Computer artwork showcases a beta DNA segment surrounded by spheres, symbolizing both innovation and interconnectedness within our genetic code. The nucleotide base matrix unveils patterns that hold profound significance in understanding hereditary traits. As we peer into abstract images of DNA molecules, we are reminded of their remarkable structure and infinite possibilities they hold for life itself. The intricacies continue with the visualization of nucleosome molecules – tiny structures that play a crucial role in organizing our genetic material. Amidst these wonders lies an HIV reverse transcription enzyme; it serves as a stark reminder of how they can shape not only life but also disease. Yet even amidst challenges, there is hope as scientists tirelessly work to decipher these complexities and find solutions. Ultimately, this captivating journey through various facets of genetics leaves us awestruck by its elegance and complexity. It reminds us that every living being carries within them an extraordinary story written in their DNA – an ancient language connecting all forms of life on Earth.