Guanine Collection
Guanine, a vital component of genetic material, plays a crucial role in the intricate world of molecular biology
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
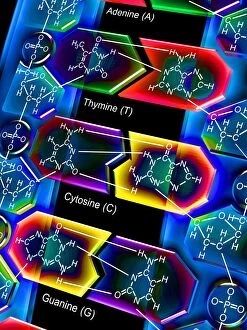
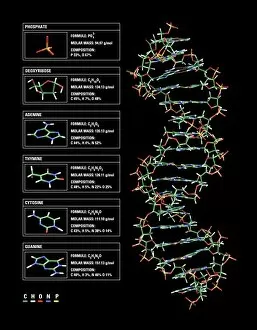
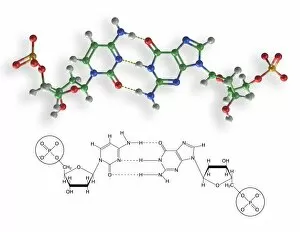
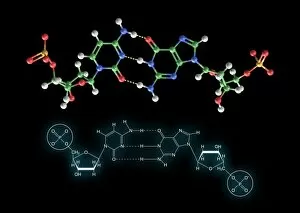
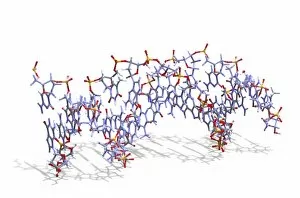
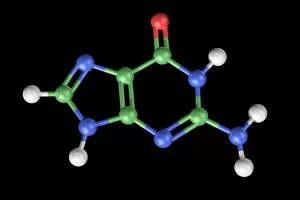
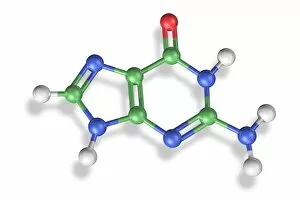
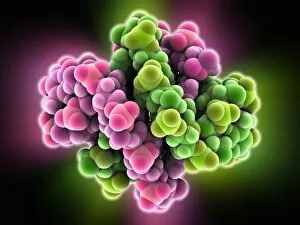
Guanine, a vital component of genetic material, plays a crucial role in the intricate world of molecular biology. As a nucleotide base matrix found in both double-stranded RNA and DNA molecules, guanine contributes to the stability and functionality of these essential structures. In scientific artwork depicting DNA molecules, guanine stands out as one of the four building blocks that form the genetic code. Its unique chemical properties enable it to pair with cytosine through hydrogen bonding, ensuring accurate replication and transmission of genetic information. The significance extends beyond laboratory experiments; it has been instrumental in various groundbreaking studies such as grapevine genome sequencing. By unraveling the complex arrangement within the grapevine's DNA molecule, scientists gain insights into its traits and potential for improvement. Artistic representations showcasing DNA structure often highlight guanine's presence alongside adenine, thymine (in DNA), or uracil (in RNA). These captivating visuals capture our fascination with this fundamental unit of life while reminding us that every living organism shares this common blueprint encoded by guanine-rich sequences. Conceptual images further emphasize how guanine intertwines with other nucleotides to create an elegant spiral staircase-like structure known as the double helix. Such depictions symbolize not only our understanding but also our awe-inspiring curiosity about nature's most extraordinary molecule – DNA. As we continue exploring the mysteries locked within each strand of DNA, let us appreciate how guanine serves as an indispensable piece in deciphering life's secrets. From its pivotal role in molecular interactions to its contribution towards scientific breakthroughs like grapevine genome sequencing, guanine remains at the forefront of biological research - forever shaping our understanding of genetics and paving new paths towards innovation.