Hearing Collection (#13)
"Hearing the Symphony of Life: From Urban Foxes to Inner Ears" Amidst the nocturnal charm of Bristol, a young urban Red fox stands on a wall
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
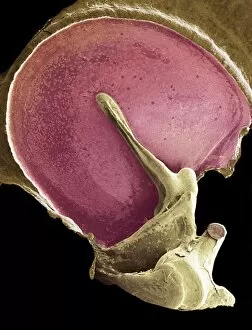
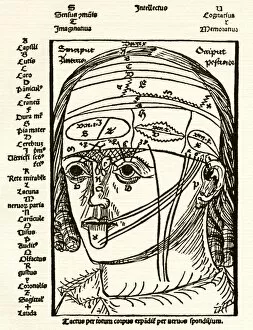
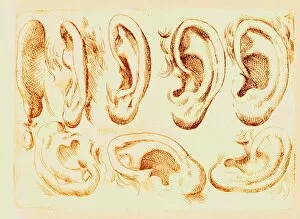
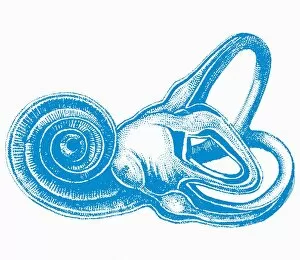
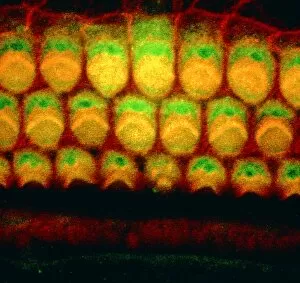
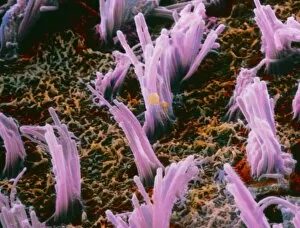
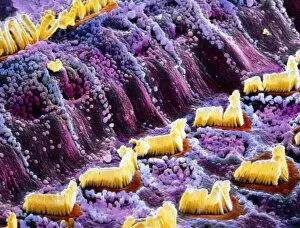
"Hearing the Symphony of Life: From Urban Foxes to Inner Ears" Amidst the nocturnal charm of Bristol, a young urban Red fox stands on a wall, its ears perked up in anticipation. Delve into the intricate world with a cross-section diagram showcasing the remarkable structure of the human ear. Explore the wonders within as we unravel a detailed diagram depicting the auditory canal, eardrum, semicircular canals, cochlea nerve, and more. Blodgetts Hearing Aid - bridging gaps between silence and sound since [insert year], empowering individuals to rediscover life's melodies. Cecil Aldin's whimsical illustration captures Tatters chasing after a car while his keen sense guides him through thrilling adventures. Transport yourself back in time as Darius I commands an audience with Persian art that beautifully portrays musicians enchanting all with their melodic tunes. London Trade Card by William Bull showcases musical instruments that have long been instrumental in harmonizing communities across generations. A young man immersed in colorful light dons headphones, allowing music to transport him beyond reality while celebrating individuality and self-expression. Unearth ancient rituals through an engraving depicting ritualistic prosecutions where sound played an integral role in cultural practices and beliefs. In Austria's meadows, an alert young hamster named Cricetus cricetus relies on acute hearing abilities to navigate its surroundings and stay vigilant against potential threats. The Whityngton Stone witnesses countless tales unfold along Holloway's streets – stories whispered from one generation to another through attentive ears over centuries past.