Hematological Collection (#4)
"Hematological Wonders: Exploring the Intricacies of Blood and Beyond" Delving into the microscopic world
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
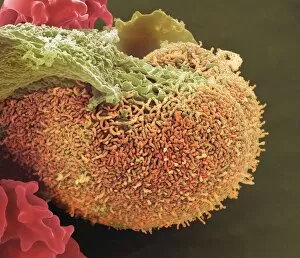
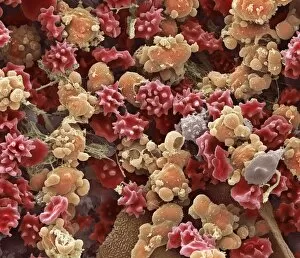
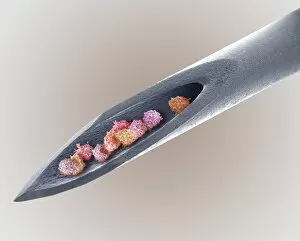
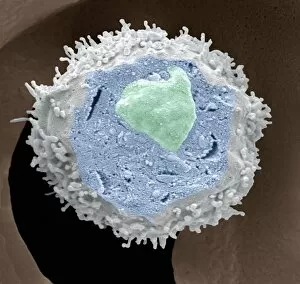
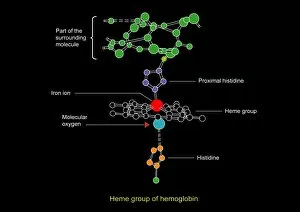
"Hematological Wonders: Exploring the Intricacies of Blood and Beyond" Delving into the microscopic world, we witness the intricate dance of white blood cells and platelets in SEM C016 / 3099. In SEM C016 / 3098, a captivating image reveals the remarkable interplay between white blood cells and platelets within our bloodstream. The monocyte white blood cell takes center stage in SEM C016 / 3089, showcasing its vital role in immune defense against pathogens. Through a light micrograph captured in C016 / 3035, we marvel at the mesmerizing beauty of red blood cells that tirelessly transport oxygen throughout our bodies. An artwork depiction (C013 / 4649) immerses us into the fascinating realm of thrombosed blood vessels, highlighting their significance in clot formation and prevention. A collection of diverse blood samples (C018 / 1034) reminds us of the invaluable insights they provide to diagnose diseases and monitor overall health. Captured under F006 / 9054, a single drop from a patient's vein holds countless secrets waiting to be unraveled by skilled hematologists worldwide. Another intriguing specimen awaits analysis as seen through F006/9055 - an enigmatic glimpse into someone's unique hematological profile lies within this precious sample. Amidst medical investigations lie unexpected discoveries; even MRI scans reveal more than meets the eye with images like "Thickened skull" (MRI scan). Haematopoietic stem cells come alive through vivid artwork, reminding us that these unsung heroes are responsible for replenishing all types of blood cells essential for life itself. Intriguingly blending artistry with scientific exploration, these captivating glimpses into hematological wonders unveil both beauty and complexity hidden beneath our skin's surface – inviting us to appreciate the remarkable world within us.