Hominid Collection (#7)
"Hominid: Unraveling the Tapestry of Human Evolution" Delving into the depths of our ancestral past, we encounter the fascinating world of hominids
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
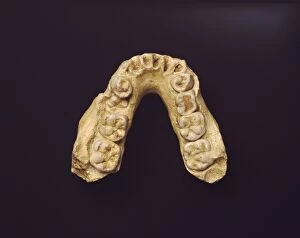
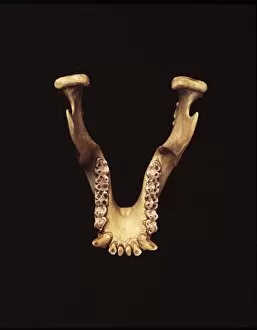
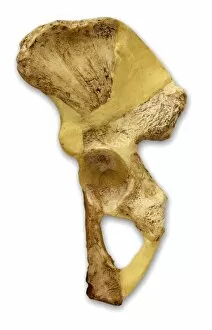
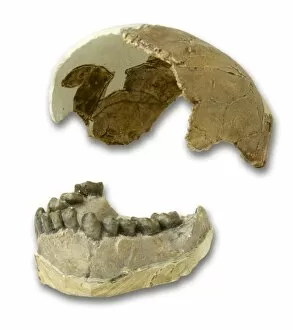
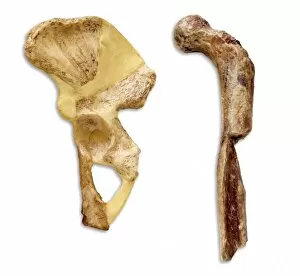
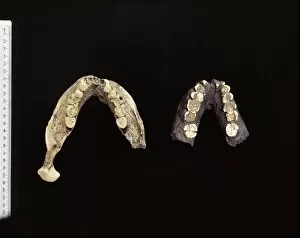
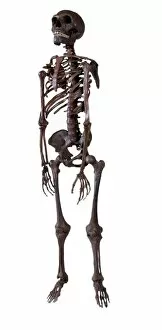
"Hominid: Unraveling the Tapestry of Human Evolution" Delving into the depths of our ancestral past, we encounter the fascinating world of hominids. These enigmatic creatures have left behind a trail of clues that offer glimpses into our own origins and evolution. One such clue is the sensory homunculus, a visual representation mapping out how different areas of our brain correspond to various parts of our body. This intricate map reveals just how interconnected and complex our sensory experiences are as hominids. Another intriguing piece in this puzzle lies within the hominid crania, ancient skulls that provide valuable insights into their physical characteristics and evolutionary progression. Among these remarkable specimens is Australopithecus afarensis (AL 288-1), affectionately known as Lucy, whose discovery shed light on early bipedalism. The famous Trail of Laetoli footprints further confirms this bipedal nature, capturing a moment frozen in time where an Australopithecus walked across volcanic ash millions of years ago. These imprints serve as tangible evidence showcasing one small step towards human-like locomotion. Examining the motor homunculus adds another layer to understanding human evolution. This depiction illustrates how different regions in our brain control specific movements throughout our bodies - a testament to the intricate coordination required for survival and adaptation. Tracing back through stages in human evolution brings us face-to-face with Australopithecus afarensis once again. Through meticulous artwork depicting these ancient beings, we can visualize their appearance and way of life during their time on Earth. Exploring further along this journey uncovers Homo neanderthalensis at Swanscombe in the UK - an opportunity to witness these close relatives engaging in daily activities firsthand through archaeological findings. Their existence serves as a reminder that multiple branches existed simultaneously during certain periods in history.