Laboratory Collection (page 4)
In the realm of scientific discovery, laboratories have served as the birthplace of countless breakthroughs and innovations
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
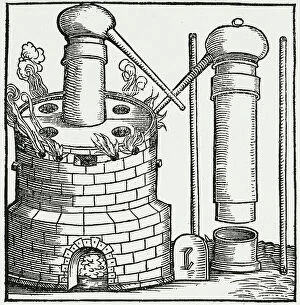
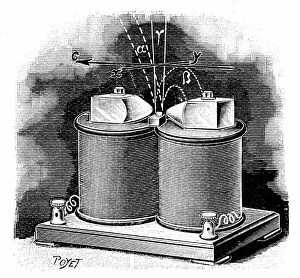
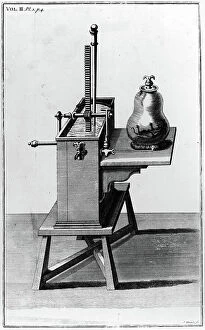
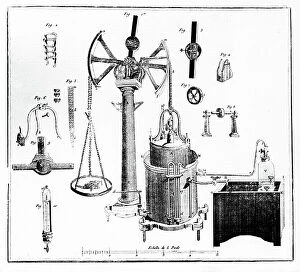
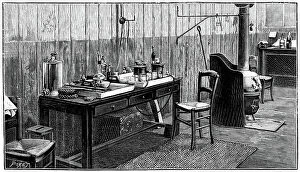
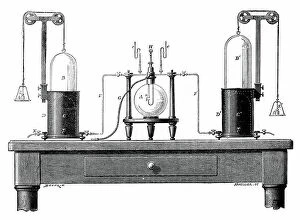
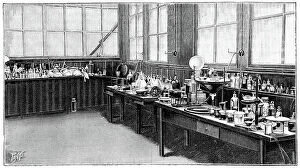
In the realm of scientific discovery, laboratories have served as the birthplace of countless breakthroughs and innovations. From the pioneering work of Rosalind Franklin in unraveling DNA's structure to Nikola Tesla's electrifying experiments, these hallowed spaces have witnessed some of history's most remarkable scientific feats. Back in 1899, Nikola Tesla's laboratory crackled with bolts of electricity discharging through the air. This visionary inventor pushed boundaries and revolutionized our understanding of electricity, paving the way for modern power systems. His laboratory became a playground for his mind-bending experiments that would shape the world we live in today. Meanwhile, Marie Curie (1867-1934) tirelessly worked in her laboratory on groundbreaking research into radioactivity. Her tireless efforts led to numerous discoveries and earned her two Nobel Prizes – one in physics and another in chemistry. Her legacy continues to inspire generations of scientists who follow in her footsteps. The laboratory is not just a place for individual brilliance; it also serves as a hub for collaborative endeavors. At CERN, home to cutting-edge particle physics research, teams working on projects like the ATLAS detector and CMS detector come together to unlock secrets about our universe’s fundamental building blocks. Science has always relied on precise measurements, which brings us to tools like mass spectrometers and tungsten carbide slip gauge blocks C016 / 2042 used within laboratories worldwide. These instruments ensure accuracy when analyzing samples or calibrating equipment—a testament to meticulousness required by scientists across disciplines. A photograph enlarger stands as an emblematic symbol within any photography lab—an essential tool that allows photographers to bring their images from small negatives into larger prints while preserving intricate details captured through lenses. Laboratory clamps serve as unsung heroes holding apparatuses firmly together during experiments—often overlooked but indispensable components ensuring safety and stability throughout various procedures conducted within these sacred spaces dedicated solely to science.