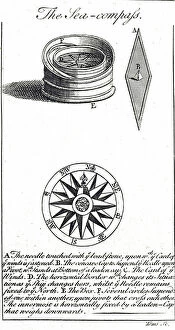
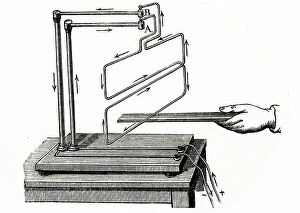
Magnetic Collection (#2)
"Magnetic: Unveiling the Invisible Forces" From its discovery in ancient China to cutting-edge fusion research, magnetic phenomena have captivated humanity for centuries
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
"Magnetic: Unveiling the Invisible Forces" From its discovery in ancient China to cutting-edge fusion research, magnetic phenomena have captivated humanity for centuries. In 1954, the mass spectrometer revolutionized scientific analysis by utilizing magnetic fields to separate ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio. Fast forward to modern times, where fusion research has taken center stage with the tokamak device. This revolutionary technology harnesses powerful magnetic fields to confine and control plasma, paving the way for limitless clean energy possibilities. Nature's own mesmerizing display of magnetism can be witnessed in the enchanting dance between Aurora borealis and Moon. The ethereal lights are a result of charged particles from solar winds interacting with Earth's magnetic field. In medical advancements, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans have become indispensable tools in diagnosing brain tumors and other ailments. By employing strong magnets and radio waves, MRI provides detailed images without harmful radiation exposure. Pushing boundaries further is the concept levitation of superconductors. This mind-boggling phenomenon defies gravity as superconductors float above powerful magnets due to their unique ability to expel all internal magnetic fields. Taking a historical turn, we recall RMS Olympic embarking on her maiden voyage in 1911 – an iconic vessel that utilized electromagnetic propulsion systems ahead of its time. Returning once again to nature's grand spectacle, witnessing Aurora borealis illuminating night skies leaves us awestruck at Earth's harmonious interaction with our planet's geomagnetic field. Beyond science and nature lies fashion inspiration; an attractive idea emerges for gents wear incorporating magnetism into design elements - a perfect blend of style and innovation that captures attention effortlessly. Pioneers like Galileo Ferraris paved the way for understanding electromagnetism through his groundbreaking discoveries during late 19th century Italy. His work laid foundations for future technological marvels we enjoy today.