Mucous Membrane Collection
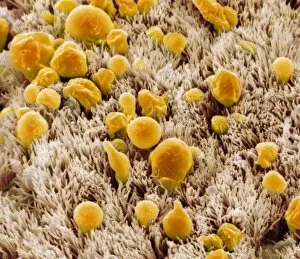
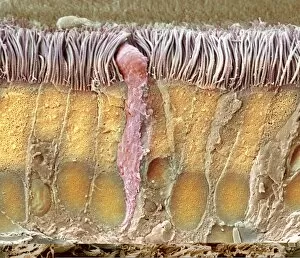
"Mucous Membrane: Exploring the Intricate Network of Protection and Function" The trachea lining, as captured in SEM images C013 / 7126 and C013 / 7122
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
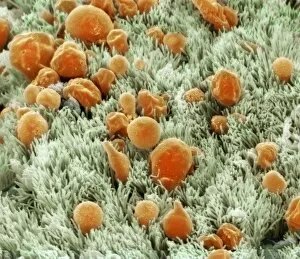
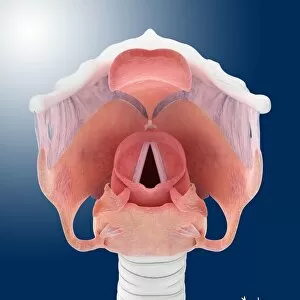
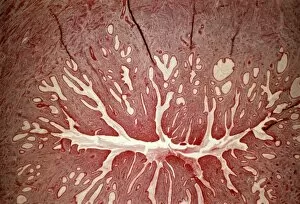
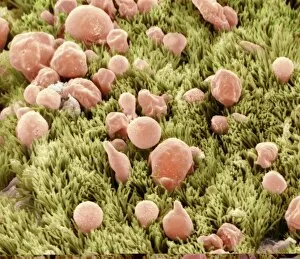
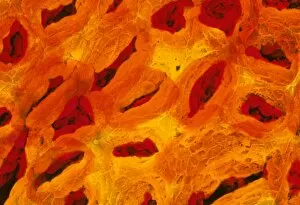
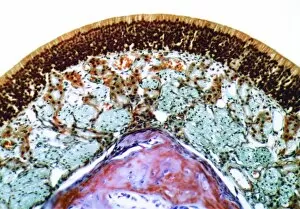
"Mucous Membrane: Exploring the Intricate Network of Protection and Function" The trachea lining, as captured in SEM images C013 / 7126 and C013 / 7122, showcases the remarkable structure of mucous membranes. These delicate yet resilient tissues line our respiratory tract, acting as a barrier against harmful particles while facilitating the exchange of oxygen. Intriguingly, even our vocal cords rely on mucous membranes to maintain their flexibility and functionality. Though not visible under a microscope like artwork depicts them, these specialized membranes play an essential role in producing sound and enabling speech. Moving beyond the realm of respiration, let's delve into another vital area where they are found - the cervix. Light micrographs such as those depicting the cervical polyp (C015 / 6744) provide us with insights into this specific region's intricate cellular composition. Additionally, endoscope views (C015 / 6738) offer a closer look at cervical polyps' appearance from within. As we explore further into SEM images C013 / 7127, C013 / 7125, C013 / 7124, and C013 / 7123 showcasing tracheal linings once again; we witness how these protective barriers adapt to different sections along our respiratory system. Their ability to secrete mucus aids in trapping foreign substances before they reach sensitive lung tissue. Lastly but equally fascinating is an image capturing rats' nose and blood vessels using SEM technology. This serves as a reminder that mucous membranes extend beyond humans; they exist across various species for similar purposes - safeguarding vital organs from potential harm. Overall, these captivating glimpses into different aspects function highlight their significance in maintaining health and well-being throughout multiple bodily systems. From defending against airborne pollutants to supporting reproductive health or facilitating vocalization – it is evident that these intricate networks deserve recognition for their indispensable roles in our bodies.