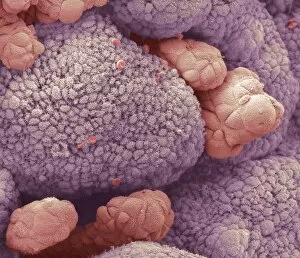
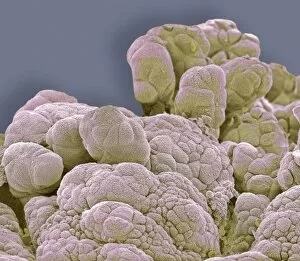
Neoplasm Collection
Neoplasm, a term encompassing various types of abnormal growths in the body, can have devastating effects on individuals
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
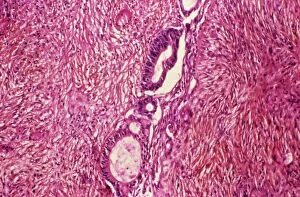
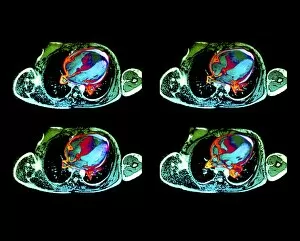
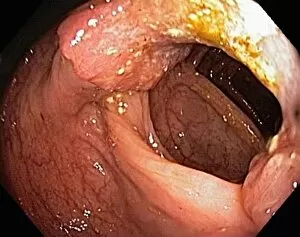
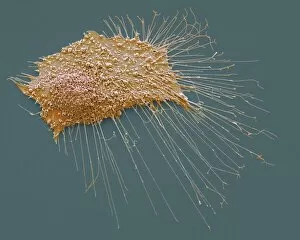
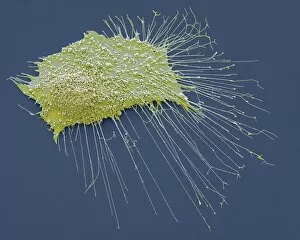
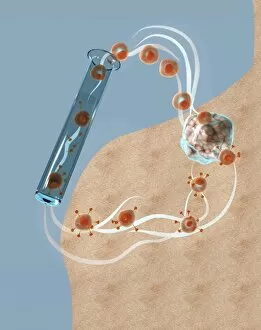
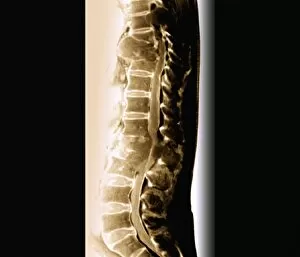
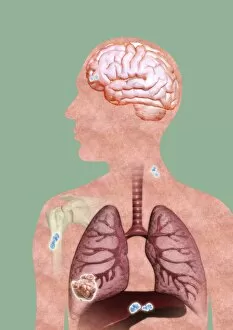
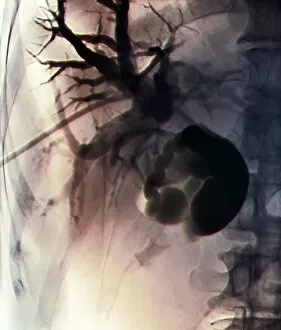
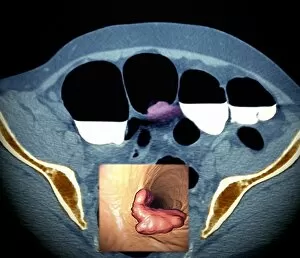
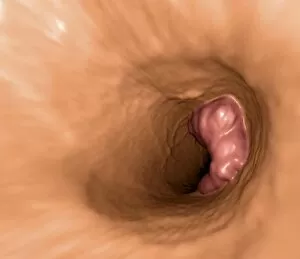
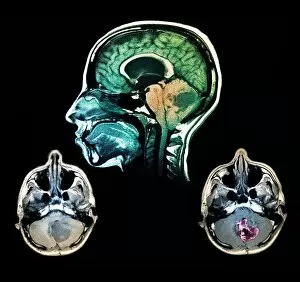
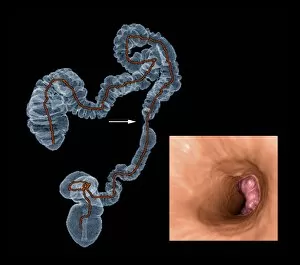
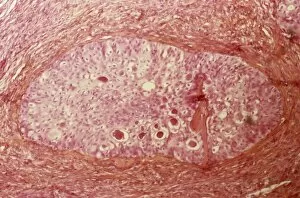
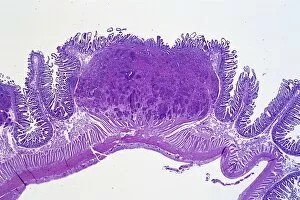
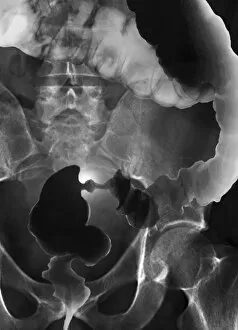
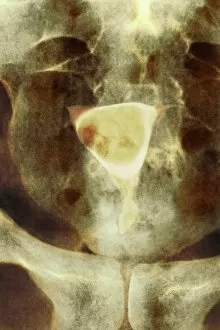
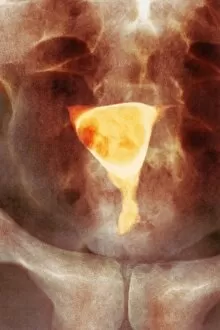
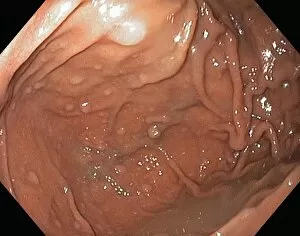
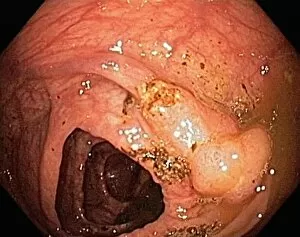
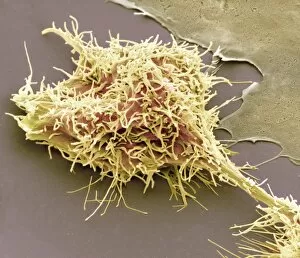
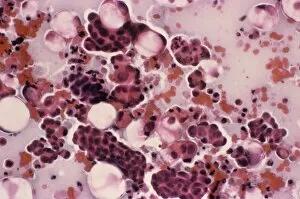
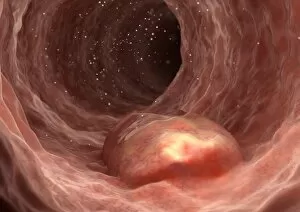
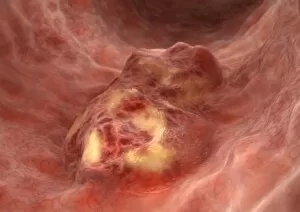
Neoplasm, a term encompassing various types of abnormal growths in the body, can have devastating effects on individuals. Ovarian cancer, one form of neoplasm, is often detected through light micrograph C015 / 7103 images that reveal the intricate cellular changes within the ovaries. Similarly, cardiac lymphoma can be observed using MRI scans that provide detailed visuals of this rare type of cancer affecting the heart. Fibroid tumors in the female uterus are another example of neoplasms that impact women's health. Understanding their anatomy is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment options. By studying these tumors closely, medical professionals can develop strategies to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Bone cancer cells are yet another manifestation of neoplastic growths that require attention. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images like F006 / 8639 and F006 / 8638 offer a closer look at these malignant cells invading bone tissue. Such visualizations aid researchers in developing targeted therapies to combat this aggressive disease. Immunotherapy has emerged as a promising approach against various forms of neoplasms. Artwork depicting this innovative treatment showcases its potential to harness the power of our immune system to fight cancer cells effectively. Unfortunately, some cancers spread rapidly throughout the body – an alarming phenomenon illustrated through artwork showing cancer cells spreading relentlessly. This emphasizes the urgent need for early detection and intervention to prevent metastasis. Spinal cancer poses unique challenges due to its location near critical nerves and tissues. Multiple MRI scans help visualize spinal tumors accurately so that healthcare providers can plan appropriate interventions tailored specifically for each patient's needs. Testicular cancer is predominantly found in young men but can affect individuals across all age groups. Light micrographs allow us to examine testicular tissue closely for any signs or abnormalities indicative of malignancy. Secondary spinal cancers occur when primary tumors from other parts spread into the spine – a situation best understood through MRI scans.