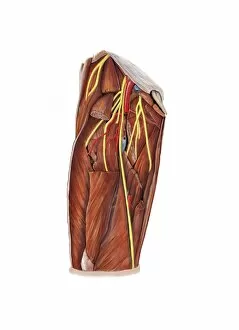
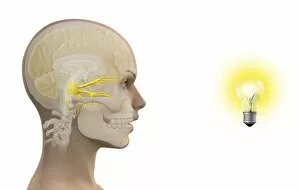
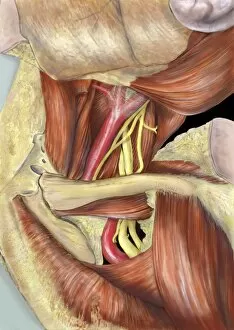
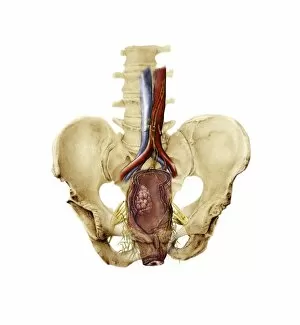
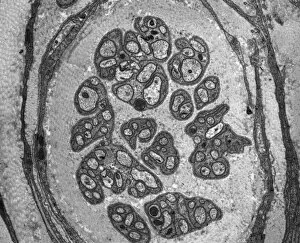
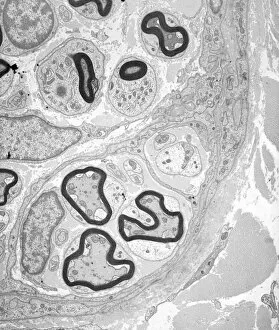
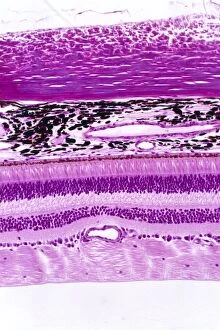
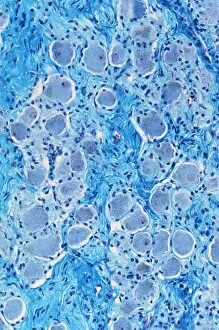
Nerves Collection (#5)
"Nerves: Unraveling the Intricacies of our Body's Communication System" Our bodies are a complex network of interconnected systems
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
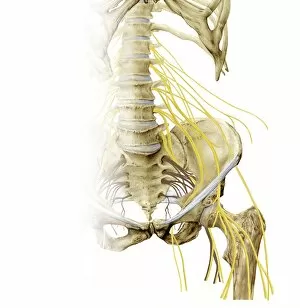
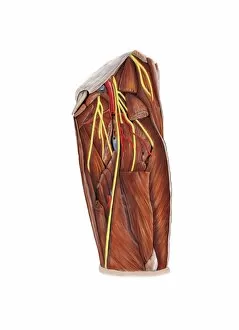
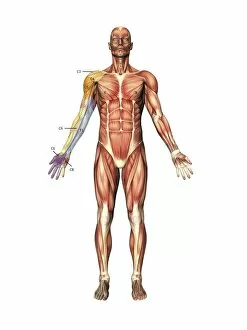
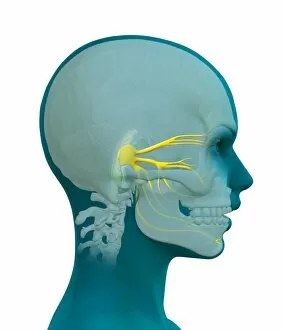
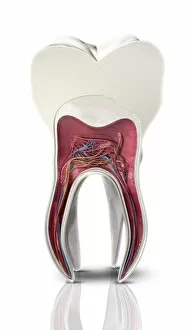
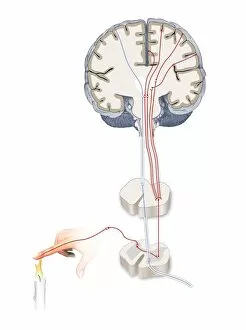
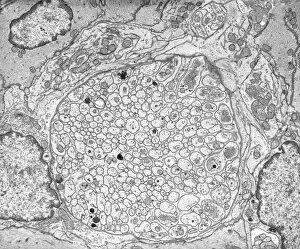
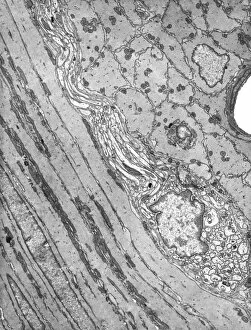
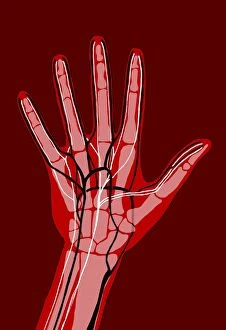
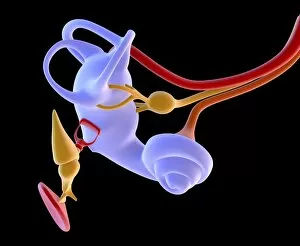
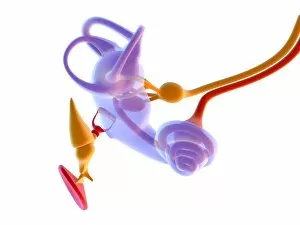
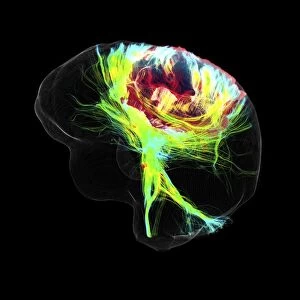
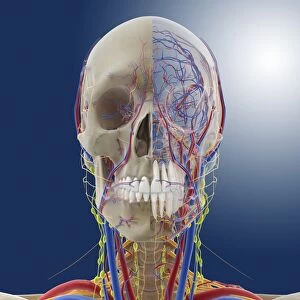
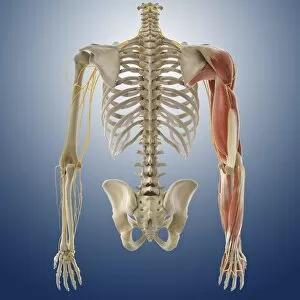
"Nerves: Unraveling the Intricacies of our Body's Communication System" Our bodies are a complex network of interconnected systems, and at the heart of it all lies our nervous system. From chakras to brain fibers, this captivating web controls every sensation we experience. Delving deeper into the mysteries, DTI MRI scans like C017/7099 and C017/7035 reveal intricate brain pathways that transmit signals throughout our body. These scans provide us with a glimpse into the fascinating world within. A diagram showcasing the human brain and spinal column reminds us of the delicate balance maintained by these vital structures, and is through these pathways that information flows seamlessly, allowing us to perceive and react to our surroundings. Even in lighthearted moments, such as a dentist cartoon by H. M. Bateman depicting cause and effect, we can see how nerves play their part in triggering reactions – both physical and emotional. The inner ear is another marvel worth exploring; its auditory canal, eardrum, semicircular canals, cochlea nerve, and eustachian tube work together harmoniously to process sound waves. Throughout history, scientists have tirelessly studied the nervous system's intricacies - an 18th-century depiction serves as a testament to humanity's enduring curiosity about this remarkable mechanism. Yet amidst all its wonders lie certain afflictions - migraines remind us that even they are sometimes falter under strain. Understanding facial nerves becomes crucial when dealing with conditions affecting expressions or sensations on our face. So next time you find yourself asking "Are you nervous?", take a moment to appreciate just how incredible your own nerve system truly is – for it enables you to feel emotions deeply while simultaneously coordinating countless bodily functions without conscious effort. Intricate yet resilient; sensitive yet powerful – our they can an awe-inspiring reminder of nature's brilliance woven within each one of us.