Neuron Collection (#15)
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Neurons: Exploring the Wonders Within Our Brain" Delving into the depths of our brain
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
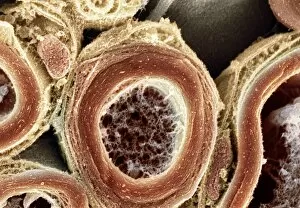
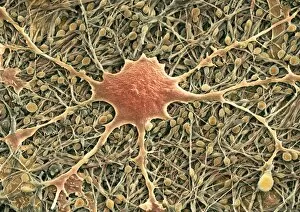
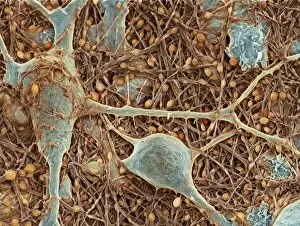
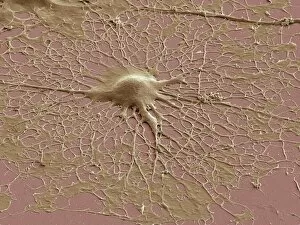
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Neurons: Exploring the Wonders Within Our Brain" Delving into the depths of our brain, we encounter a histological diagram of a mammalian retina. This intricate network showcases the complexity and beauty of neurons that enable us to perceive light and color. Moving further, we explore cerebellum tissue through a light micrograph. The mesmerizing patterns reveal nerve and glial cells working in harmony, orchestrating our body's movements with precision. Zooming in closer, we witness a synapse nerve junction captured by TEM. This microscopic marvel highlights how information is transmitted between neurons, forming connections crucial for our thoughts and actions. Shifting gears to SEM imagery, we are introduced to an awe-inspiring nerve cell. Its intricate structure resembles an elaborate work of art—a testament to nature's ingenuity in crafting these building blocks of intelligence. Tracing back history, we stumble upon Santiago Ramon y Cajal's 1894 drawing depicting cell types within the mammalian cerebellum. His meticulous observations laid foundations for understanding neural networks that govern our motor skills. Venturing deeper into brain tissue, we discover hippocampus tissue—an essential region responsible for memory formation and spatial navigation. Here lies another realm where neurons weave together memories that shape who we are. Intriguingly unique are Purkinje nerve cells found within the cerebellum—majestic giants among their peers. Their distinctive appearance signifies their vital role in coordinating movement and maintaining balance. As if peering through a microscope lens once again, another nerve cell captures our attention—the epitome of elegance amidst complexity; it reminds us how intricately woven life truly is at its core. Diving into glial stem cell culture under bright illumination reveals their remarkable regenerative potential—a beacon of hope for treating neurological disorders as they hold promises yet untapped. Examining brain tissue blood supply uncovers an indispensable lifeline, nourishing neurons with oxygen and nutrients.