Neurones Collection (#4)
Neurons, the building blocks of our nervous system, play a crucial role in transmitting information throughout our bodies
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
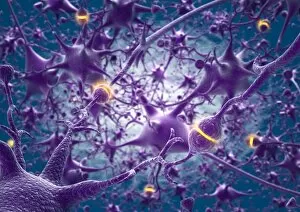
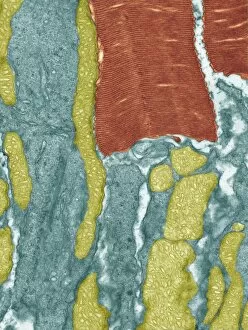
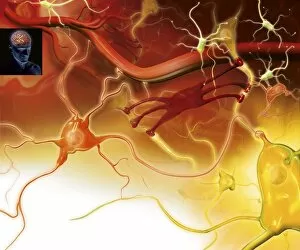
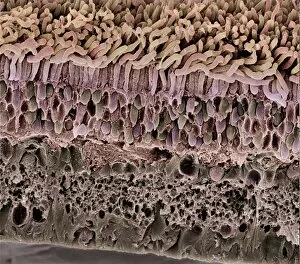
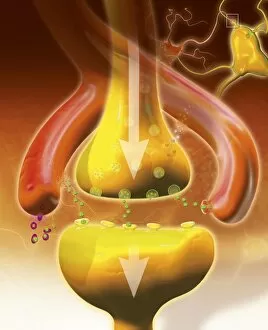
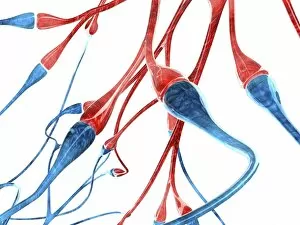
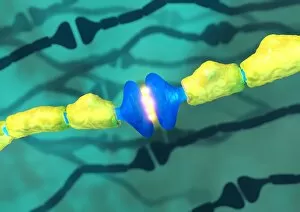
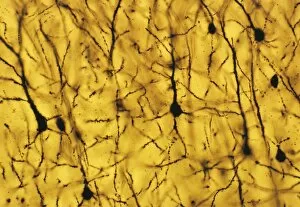
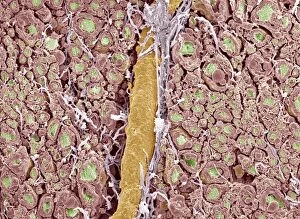
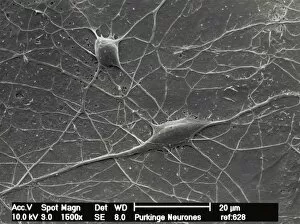
Neurons, the building blocks of our nervous system, play a crucial role in transmitting information throughout our bodies. These remarkable cells come in various shapes and sizes, each with its own unique function. In a mesmerizing light micrograph, nerve and glial cells are intricately intertwined like a complex network. The delicate synapse nerve junctions captured by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) reveal the microscopic connections that allow neurons to communicate with one another. Glial stem cell culture, seen through another light micrograph, showcases the incredible regenerative potential of these unsung heroes. They possess the ability to differentiate into different types of glial cells which support and protect neurons. Examining brain tissue blood supply under the microscope reveals an intricate web of vessels nourishing this vital organ. This lifeline ensures that neurons receive oxygen and nutrients necessary for their proper functioning. Another captivating image shows neural stem cell culture - a glimpse into the fascinating world of neurogenesis where new neurons are born. This process holds immense promise for understanding brain development and treating neurological disorders. Zooming closer into cerebral cortex nerve cells brings forth their intricate structure and complexity. These specialized neurons enable us to think, reason, learn, and perceive the world around us. Even tiny creatures like C. Elegans worms have their neuronal beauty revealed through light microscopy; they serve as valuable models for studying fundamental aspects of neuroscience research. Motor neurons depicted in yet another stunning light micrograph remind us how essential they are for coordinating movement throughout our body - from simple reflexes to complex actions requiring precision control. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) offers an up-close look at individual nerve cells' ultrastructure: revealing their organelles such as mitochondria or Golgi apparatus within them – all working together harmoniously to ensure proper neuronal function Synapse nerve junctions imaged using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showcase nature's architectural marvels - these minute structures facilitate rapid communication between neighboring neurons. Lastly, a captivating SEM image captures the intricate beauty of nerve cells themselves.