Nucleus Collection (#21)
"The Nucleus: Unveiling the Mysteries of Life's Command Center" Exploring the intricate world within our cerebellum tissue
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
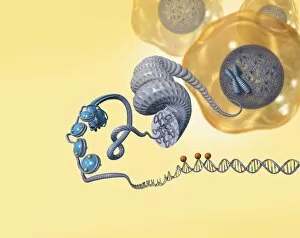
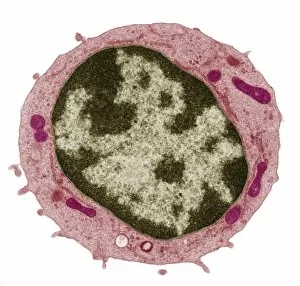
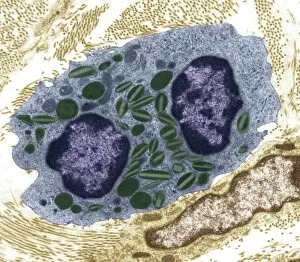
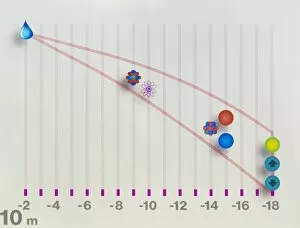
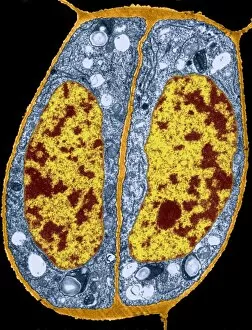
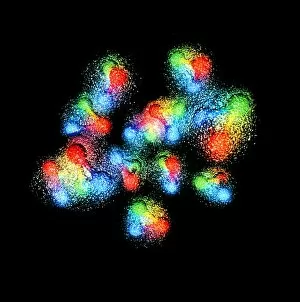
"The Nucleus: Unveiling the Mysteries of Life's Command Center" Exploring the intricate world within our cerebellum tissue, where the nucleus orchestrates every movement and balance. A mesmerizing light micrograph reveals the nucleus at the heart of M51 Whirlpool Galaxy, a cosmic dance guided by its gravitational pull. Witnessing life's beginning through a budding yeast cell, as its nucleus holds the blueprint for growth and reproduction. Delving into the secrets of communication with a nerve cell captured in stunning detail through SEM imaging, showcasing its complex nucleus. Behold the majestic Sombrero Galaxy (Messier 104), where billions of stars revolve around their central nucleus like celestial dancers in perfect harmony. The hippocampus brain tissue unveils memories etched within each neuron's nucleus, shaping who we are and what we remember. Peering into HeLa cells under a light microscope (C017/8299), revealing their remarkable nuclei that have revolutionized medical research. An artistic representation takes us deep into Medulla Oblongata's core—the vital center controlling essential bodily functions—where nuclei reign supreme. Captivating artwork depicts nuclear fission—a powerful force harnessed to generate energy while reminding us of its immense potential and responsibility. Marvel at NGC 4258 spiral galaxy's galactic light show, where vibrant colors illuminate star clusters revolving around their radiant nuclear core. Human cells come alive under scrutiny as their nuclei hold genetic information that shapes our unique characteristics and existence itself. Exploring kidney tubules in section unravels an intricate network governed by countless tiny nuclei working harmoniously to maintain our body’s equilibrium. Intricate yet awe-inspiring, these glimpses into various realms remind us that no matter how vast or minuscule, from galaxies to microscopic cells - all bow to the commanding presence of the nucleus.