Organelles Collection (#4)
Organelles are the tiny structures within cells that perform specific functions, much like organs in our body
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
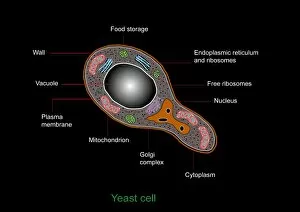
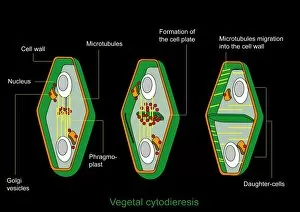
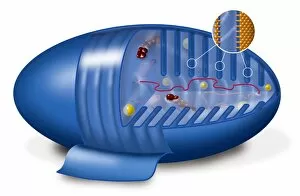
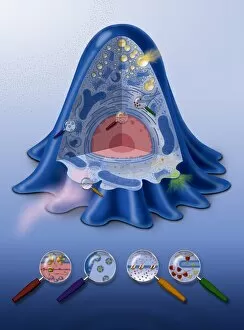
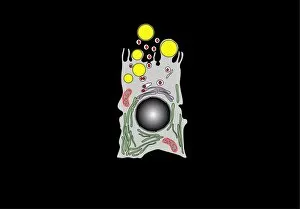
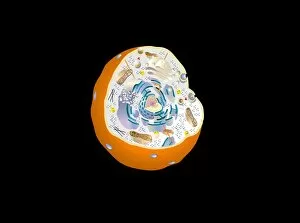
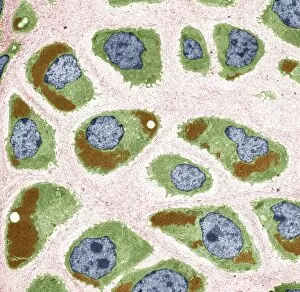
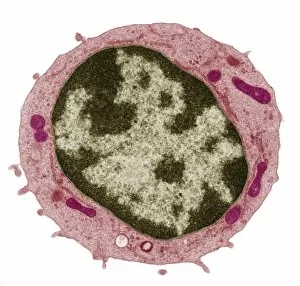
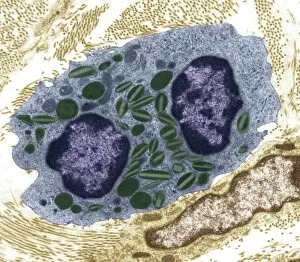
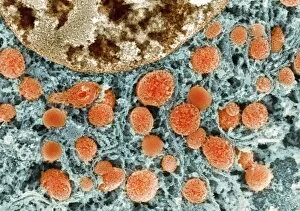
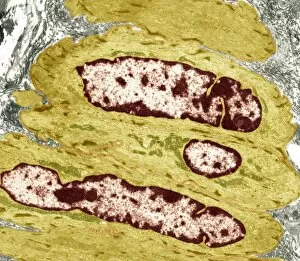
Organelles are the tiny structures within cells that perform specific functions, much like organs in our body. They play a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and functionality of cells. Let's take a closer look at some fascinating organelles through various artistic representations and microscopic images. The rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an extensive network of membranes involved in protein synthesis and transport within cells. In a stunning transmission electron microscopy (TEM) image, we can witness its intricate structure resembling a maze, highlighting its importance in cellular processes. Different cell types exhibit unique characteristics, as beautifully depicted through artwork. One such example is the Trypanosome protozoan, an intriguing single-celled organism with flagella that causes African sleeping sickness. Its distinct shape captured in artwork showcases its remarkable adaptability to survive within hosts. Nerve cells are vital for transmitting electrical signals throughout our bodies. TEM images provide us with breathtaking glimpses into their complex structure - long branching extensions called dendrites and axons covered by myelin sheaths - enabling efficient communication between neurons. Plasma cells are specialized immune cells responsible for producing antibodies to fight infections. A TEM image reveals their characteristic appearance with abundant rough ER indicating high protein synthesis activity, emphasizing their critical role in immunity. Another essential organelle is the Golgi apparatus, which modifies and packages proteins for transportation within or outside the cell. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) provides detailed views of this organelle's stacked membrane discs resembling pancakes - an architectural marvel. Purkinje nerve cells found in the cerebellum coordinate movement control; they possess elaborate dendritic trees allowing them to receive vast amounts of information from other neurons. TEM captures these intricacies perfectly, showcasing their significance for motor coordination. Fibroblast cells contribute to tissue repair by synthesizing extracellular matrix components like collagen fibers. Artwork representing fibroblasts highlights their elongated shape and their role in maintaining tissue integrity.