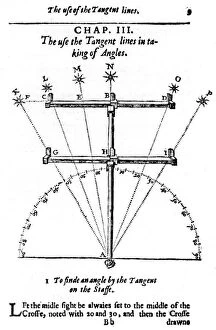
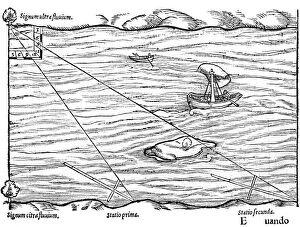
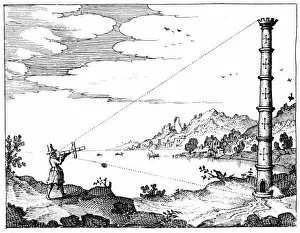
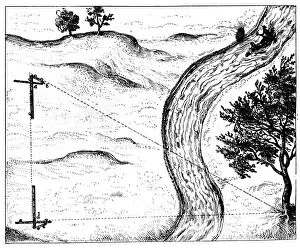
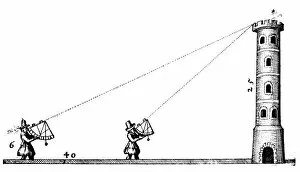
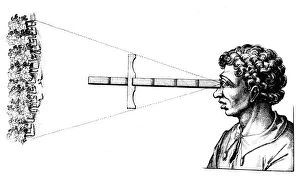
Oxford Science Archive Collection (#3)
"Exploring the Vast Oxford Science Archive: A Journey Through Time and Discoveries" Step into a world where history intertwines with scientific breakthroughs
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
"Exploring the Vast Oxford Science Archive: A Journey Through Time and Discoveries" Step into a world where history intertwines with scientific breakthroughs, as we delve into the captivating Oxford Science Archive. From the early days of locomotives to groundbreaking astronomical observations, this collection showcases humanity's relentless pursuit of knowledge. Witness the awe-inspiring sight of a train crossing Stockport viaduct on the London & North Western Railway in 1845, symbolizing mankind's determination to conquer distance and connect nations. Marvel at our understanding of celestial bodies through stunning images capturing Jupiter's four moons - Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto - observed in 1979. Travel back further in time to 1867 when The Engineer publication chronicled technological advancements that shaped society. Immerse yourself in an era when engineering marvels like the Great Eastern ship were constructed on the banks of Thames at Millwall in 1857. Meet James Watt, a Scottish engineer whose inventive genius revolutionized steam power during the Industrial Revolution. His portrait from 1833 serves as a reminder of human ingenuity that propelled us forward. Explore artistry intertwined with science as you encounter Benjamin Waterhouse Hawkins' depiction of "The Whale" circa 1850 – a testament to both artistic skill and zoological exploration. Encounter JJ Thomson, British nuclear physicist extraordinaire captured in an iconic photograph from 1898 – his work paving the way for modern atomic theory. Reflect upon mankind's relationship with nature through poignant imagery depicting water scarcity amidst abundance titled "Water. Water. Everywhere; and not a Drop to Drink" from 1849. Witness progress etched into landscapes such as Tring cutting on London & Birmingham Railway (1837) or Kilsby Tunnel construction (1839), showcasing how infrastructure transformed societies. Acknowledge both triumphs and challenges faced by humanity throughout history as industrial pollution looms over Sheffield Yorkshire in the 1920s.