Peripheral Collection
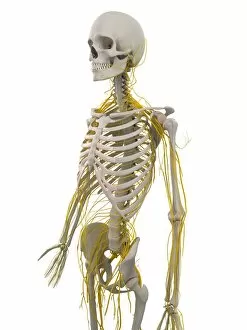
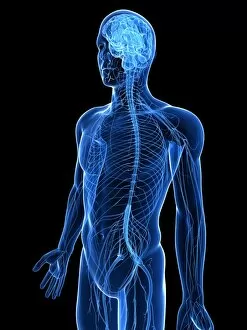
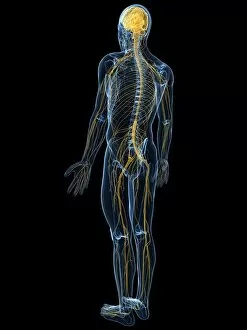
The peripheral nervous system plays a vital role in our body, connecting the central nervous system to various parts of our anatomy
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
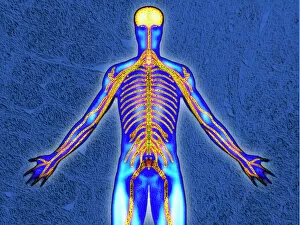
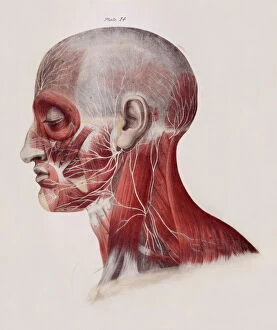
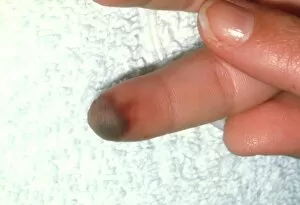
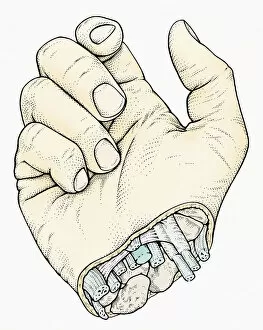
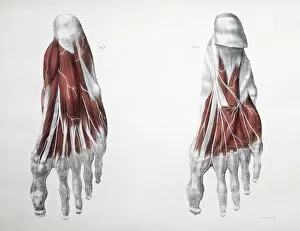
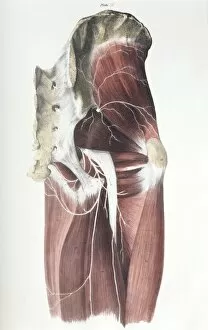
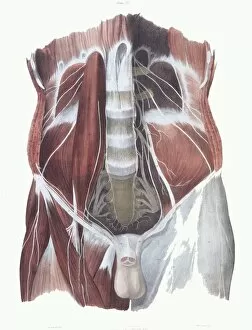
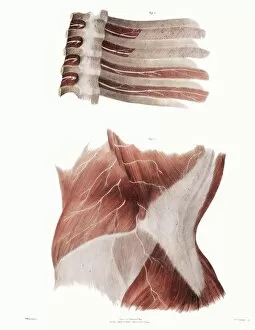
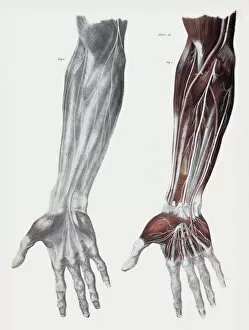
The peripheral nervous system plays a vital role in our body, connecting the central nervous system to various parts of our anatomy. It consists of nerves that branch out from the brain and spinal cord, reaching every corner of our being. One aspect of the peripheral nervous system is its involvement in facial expressions. The intricate network of facial nerves allows us to convey emotions through smiles, frowns, and everything in between. These tiny fibers work together like puppet strings, bringing life to our expressions. Another intriguing feature is peripheral vasoconstriction, which can be observed by examining a patient's finger. When this occurs, blood vessels narrow down due to signals from the sympathetic nervous system. This phenomenon helps regulate body temperature and maintain blood pressure. Illustrations showcasing peripheral nerves reveal their complex structure consisting of ganglia (clusters of nerve cell bodies), nerve fibers transmitting messages at lightning speed, myelin sheaths protecting these delicate fibers, arteries supplying oxygenated blood for energy production within cells, veins carrying away waste products for elimination, and fat cells providing insulation. Zooming into a cross-section at the wrist reveals an intricate web formed by arteries, veins, and nerves within our hands. This illustration highlights how crucial these structures are for sensory perception and motor control. In today's digital age where technology reigns supreme, peripherals have become indispensable tools for human-computer interaction. From mouse connectors to Apple joysticks showcased at computer museums or fire stations equipped with advanced LCC-MFB systems - they all rely on precise communication between devices via the somatic peripheral nervous system. A close-up view of a computer keyboard reminds us how interconnected we are with technology as we navigate through countless tasks using just fingertips dancing across keys. Similarly essential is the trusty computer mouse that aids in seamless navigation on screens large or small. Whether it's clicking away on a mouse or typing furiously on keyboards – peripherals bridge gaps between humans and machines effortlessly thanks to the peripheral nervous system.