Pharmaceutics Collection (#10)
Pharmaceutics, the art and science of creating life-saving medications, is a fascinating field that encompasses various aspects of chemistry, biology, and medicine
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
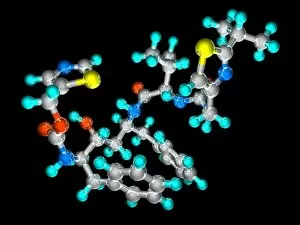
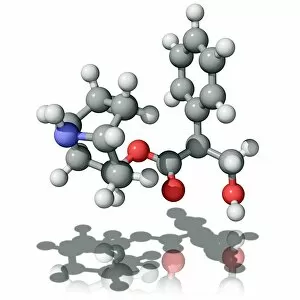
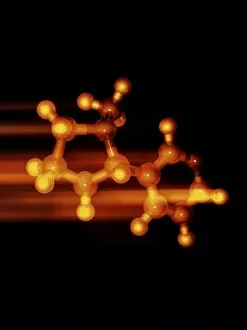
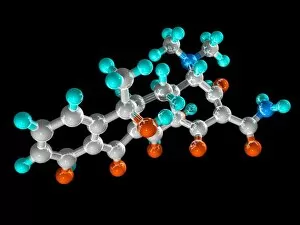
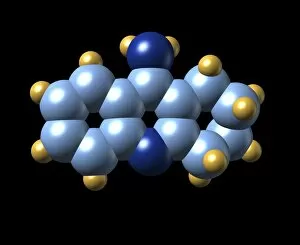
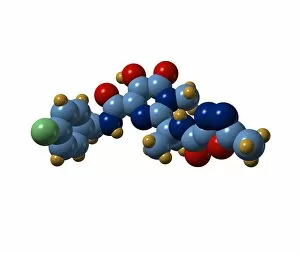
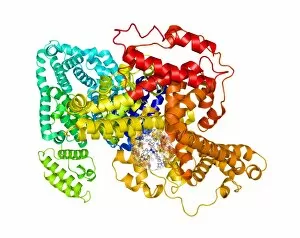
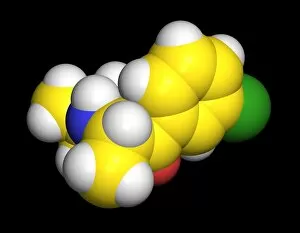
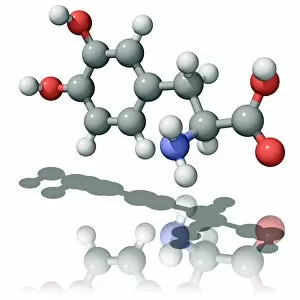
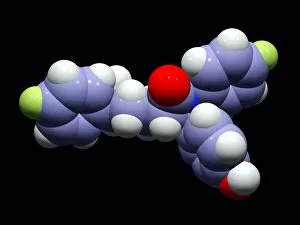
Pharmaceutics, the art and science of creating life-saving medications, is a fascinating field that encompasses various aspects of chemistry, biology, and medicine. From the intricate insulin molecule to satirical artwork depicting medical prescriptions, pharmaceutics combines creativity with scientific precision. In the realm of diabetes treatment, Januvia's diabetes drug molecule stands as a beacon of hope for millions worldwide. Similarly, Praziquantel parasite drug fights against harmful parasites plaguing vulnerable populations. The two forms of thalidomide remind us of the importance of thorough testing and regulation in pharmaceutical development. While one form caused tragic birth defects in the past, its other variant has found utility in treating certain conditions today. Isotretinoin anti-acne drug offers relief to those struggling with persistent skin issues. Its molecular structure represents years of research aimed at combating acne effectively. Mescaline hallucinogenic drug molecule delves into another facet where pharmaceutics intersects with human perception and consciousness exploration. This compound holds cultural significance for some communities due to its mind-altering properties. Valdecoxib anti-inflammatory drug provides solace to individuals battling chronic pain by reducing inflammation within their bodies. Paclitaxel drug molecule showcases advancements in cancer treatment through targeted therapies that attack malignant cells directly. Stepping back into history reveals an old pharmacy adorned with reproductions from ancient laboratories—a testament to how far we've come since Nicholas Culpeper's time. Culpeper himself was an English physician who contributed significantly to herbal medicine practices during his era. Through these diverse examples, pharmaceutics emerges as a dynamic discipline that continually strives towards improving global health outcomes while honoring our rich medicinal heritage.