Photosynthesis Collection (page 5)
"Unveiling the Marvels of Photosynthesis: From Chloroplasts to Sunflowers" In the intricate world of plants
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
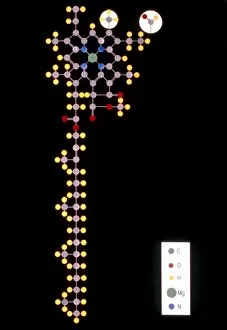
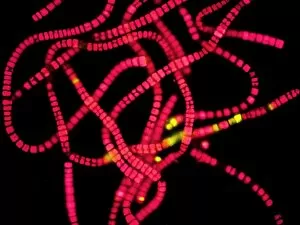
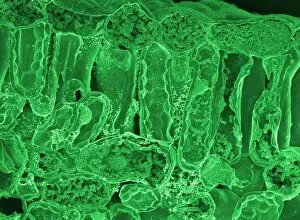
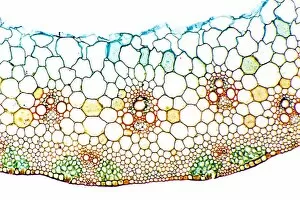
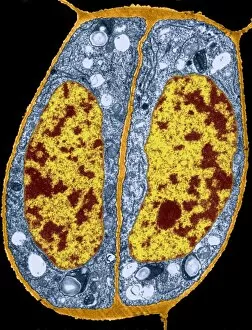
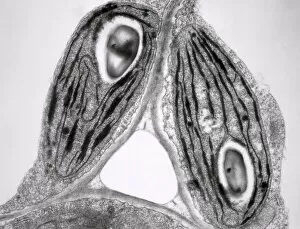
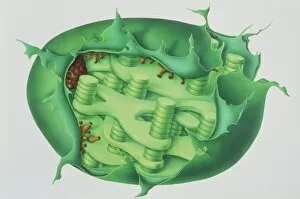
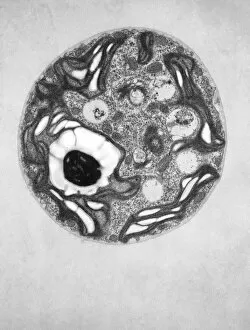
"Unveiling the Marvels of Photosynthesis: From Chloroplasts to Sunflowers" In the intricate world of plants, a pea plant's cell holds a secret powerhouse known as chloroplast. These tiny green structures work tirelessly, converting sunlight into energy through the process of photosynthesis. Nature's artistic touch can be witnessed in mesmerizing patterns etched on sandy shores by mint-sauce worms, scientifically named Symsagittifera roscoffensis or Convoluta, and is awe-inspiring to think that these delicate creatures contribute to the grand cycle of life. Delving deeper into chloroplast structure reveals an exquisite artwork crafted by nature itself. Picture No. 11675585 captures this creation beautifully, showcasing its conceptual image and highlighting its significance in sustaining life on Earth. Traveling across continents, we encounter the Hawaiian Laua e fern, Microsorum grossum, which found its way to Hawaii and thrives in Aneho omalu Bay. This resilient fern reminds us of nature's adaptability and resilience against all odds. The iconic sunflower stands tall against a radiant sun backdrop in c. 1945 oil painting—a timeless symbol representing beauty and vitality intertwined with photosynthesis' essence—the ability to harness solar energy for growth and survival. Exploring Spain's Balearic Islands brings us face-to-face with the vibrant crown daisy flower (Glebionis coronarium). Its petals basked under warm European sunlight remind us that even small blooms play their part in sustaining our ecosystem. Venturing further westward takes us to Providence, Rhode Island—where yellow marigolds joyfully soak up every ray of sunshine they can find. Their bright hues serve as a reminder that photosynthesis not only fuels life but also adds color and vibrancy to our surroundings. A serene forest scene unfolds in Upper Bavaria, Germany when encountering Lady Fern (Athyrium filix-femina).