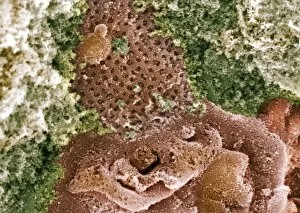
Podocytes Collection
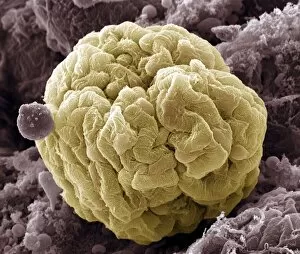
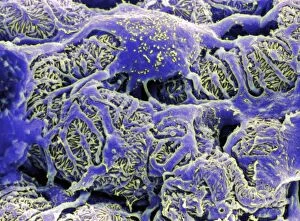
Podocytes are specialized cells found in the kidney glomerulus, which play a crucial role in the process of filtration
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
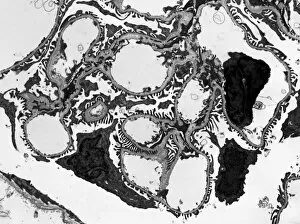
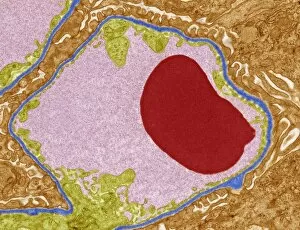
Podocytes are specialized cells found in the kidney glomerulus, which play a crucial role in the process of filtration. These unique cells have intricate structures that enable them to efficiently filter waste products and excess fluids from our blood. When observed under a scanning electron microscope (SEM), the kidney glomerulus appears as a complex network of tiny blood vessels intertwined with podocyte-covered capillaries. The SEM images reveal the delicate architecture of these filtration units, showcasing their importance in maintaining renal function. In contrast, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) provides a more detailed view at an ultrastructural level. TEM images display the fine intricacies of these cells, highlighting their foot-like extensions called pedicels that interlock to form filtration slits. These slits act as selective barriers, allowing small molecules like water and ions to pass through while preventing larger substances such as proteins from escaping into urine. One particular TEM image labeled C016/5831 showcases the remarkable arrangement within the kidney glomerulus. This specific image captures their precise positioning and interconnectedness, emphasizing their vital role in facilitating efficient filtration processes. The SEM images further emphasize this significance by displaying multiple views of kidney glomeruli covered with numerous podocyte cells. These captivating visuals highlight how these specialized cells work together to ensure effective waste removal and maintain fluid balance within our bodies. Overall, studying podocytes using various microscopic techniques provides valuable insights into understanding renal physiology and pathology. By unraveling their intricate structure and function through SEM and TEM imaging methods, scientists can gain deeper knowledge about kidney health and develop innovative treatments for diseases affecting these essential filtering units.