Rameses Collection (#8)
Discover the timeless legacy of Rameses, the mighty pharaoh who left his mark across ancient Egypt and beyond
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
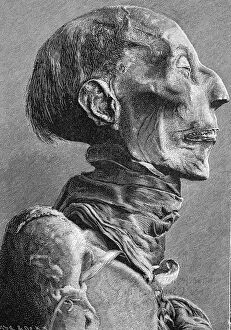
Discover the timeless legacy of Rameses, the mighty pharaoh who left his mark across ancient Egypt and beyond. From the grandeur of Piazza del Popolo in Rome to the awe-inspiring Temple of Ramses III in Abu Simbel, Rameses' influence can be felt far and wide. In Rome's Piazza del Popolo, a statue pays homage to Rameses III, a revered ruler whose mummy still captivates historians today. Step into the Temple of Ramses III and witness his majestic presence as he dons the Khepresh crown, symbolizing his power and authority. Travel further into Egypt's rich history at Abu Simbel, where the illuminated facade of the Small Temple of Hathor stands as a testament to Queen Nefertari's devotion. Marvel at giant limestone statues depicting Rameses II holding both crook and flail - symbols of his leadership and prosperity. The Great Temple II in Aswan showcases this pharaoh's architectural prowess with its imposing structure that has stood for centuries. Explore further into Thebes at the remarkable Ramesseum, dedicated to immortalizing Rameses II's reign through intricate carvings and towering columns. Witness colossal figures honoring Ramesses II himself at Abu Simbel - an extraordinary sight that leaves visitors in awe. And let us not forget about Sphinx from Rameses II period; an enigmatic guardian shrouded in mystery yet embodying strength and wisdom. Ramseses' enduring legacy lives on through these magnificent structures scattered across Italy and Egypt. Immerse yourself in their splendor as you journey back in time to unravel the mysteries surrounding one of history’s most influential rulers.