Refraction Collection (#8)
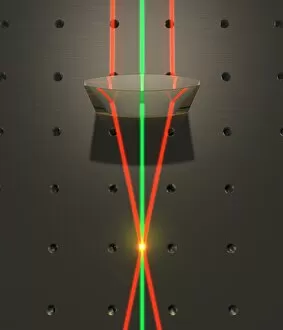
Refraction: Unveiling the Mysteries of Light In the realm of science, it has long been a captivating phenomenon
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
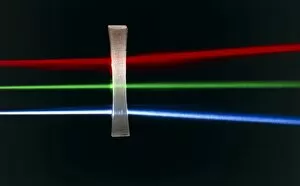
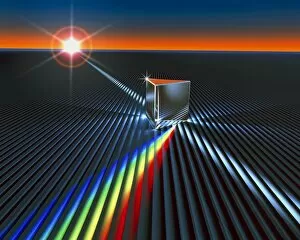
Refraction: Unveiling the Mysteries of Light In the realm of science, it has long been a captivating phenomenon. Dating back to the 17th century, René Descartes' optics theory shed light on this intriguing concept. Through his experiments with copper and magnesium sulphate, he unraveled the secrets behind how light bends as it passes through different mediums. Imagine peering into a microscope and witnessing the mesmerizing beauty of copper sulphate crystals under high magnification (LM). Their intricate patterns seem to dance before your eyes, showcasing nature's artistic prowess. Venturing beyond laboratories, let us dive into Armenime Cove's turquoise waters where a graceful Green Turtle (Chelonia mydas) glides effortlessly over volcanic sandy bottoms. As sunlight penetrates the water's surface, refraction transforms its path, creating an ethereal spectacle that enchants both divers and marine life alike. Isaac Newton's prism experiment comes to mind—a groundbreaking illustration depicting white sunlight splitting into various colors when passing through a prism (co). This revelation revolutionized our understanding of light and paved the way for further exploration in optics. Pierre de Fermat enters our narrative—an influential figure whose caricature captures his contribution to unraveling mysteries related to refraction (C015 / 6714). His work laid foundations for comprehending how light interacts with matter at molecular levels—unveiling molecular orbitals that govern these interactions. Returning to those enchanting copper sulphate crystals under microscopic observation (LM), we are reminded once again of their role in deepening our knowledge about refraction. These tiny structures hold within them vast insights into how light behaves when traversing different substances. As we journey across continents, we find ourselves amidst Brazil's Amazonia region—home to one of Earth's most enigmatic creatures—the Amazon river dolphin (Inia geoffrensis).