Rna Polymerase Collection
RNA polymerase is a crucial enzyme involved in the replication and transcription of genetic material
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
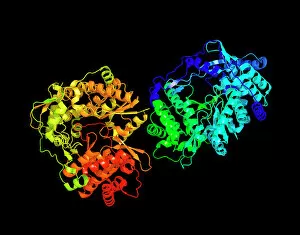
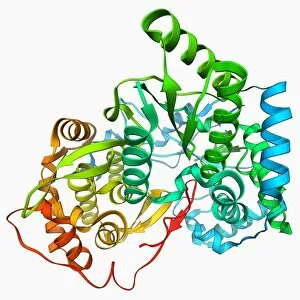
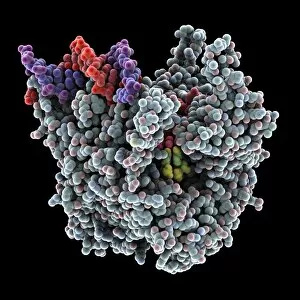
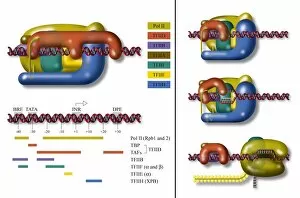
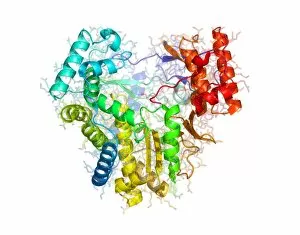
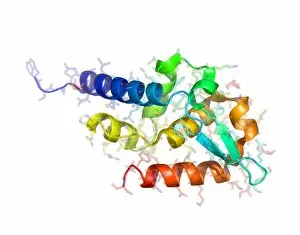
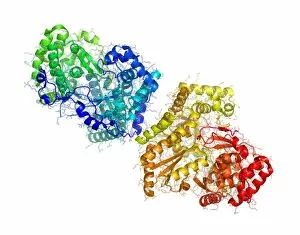
RNA polymerase is a crucial enzyme involved in the replication and transcription of genetic material. Specifically, it plays a significant role in the Hepatitis C virus life cycle. This remarkable molecule, represented by its molecular model, holds the key to understanding how this deadly virus operates. In DNA transcription, illustrated as C018 / 0900, RNA polymerase acts as a catalyst for converting DNA into RNA. It unwinds the double helix and synthesizes an RNA strand complementary to one of the DNA strands. This process is essential for gene expression and protein synthesis. The Hepatitis C polymerase enzyme (F006 / 9427) further highlights its significance in viral replication. By replicating the viral genome accurately, this enzyme ensures that new infectious particles are produced efficiently within host cells. Another critical player in gene regulation is the gene activator protein (F006 / 9406). Working alongside RNA polymerase, it enhances transcription by binding to specific regions of DNA called enhancers or promoters. The intricate structure can be seen through various depictions such as artwork showcasing RNA polymerase transcription and genetic molecular mechanisms. These illustrations provide insights into how this complex machinery orchestrates precise copying of genetic information during transcription. Understanding initiation complex formation during transcription becomes clearer with diagrams like the Transcription Initiation Complex diagram. It illustrates how multiple proteins assemble at specific sites on DNA to initiate mRNA synthesis under the guidance of RNA polymerase. Different viruses also possess their own versions of RNA polymerases; examples include Norwalk virus and rabies virus (RNA Polymerases from Norwalk Virus & Rabies Virus). The study of these unique enzymes helps unravel distinct mechanisms employed by diverse pathogens during infection. Ultimately, studying Hepatitis C virus's dedicated RNA polymerase enzyme sheds light on potential therapeutic targets against this devastating disease. With ongoing research focused on inhibiting or disrupting this vital enzymatic activity, we move closer towards finding effective treatments for Hepatitis C.