Rna Virus Collection (#4)
RNA viruses are a diverse group of infectious agents that have captured the attention of scientists and researchers worldwide
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
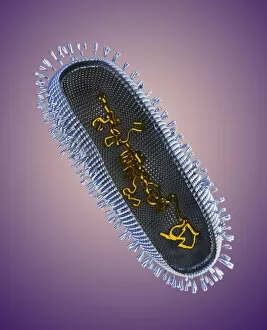
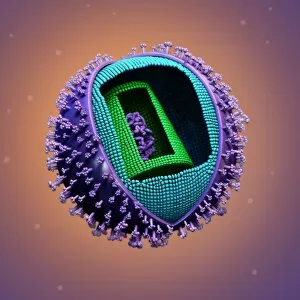
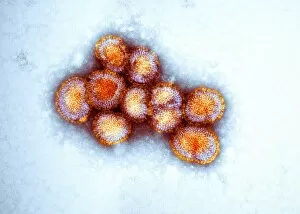
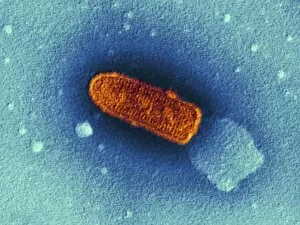
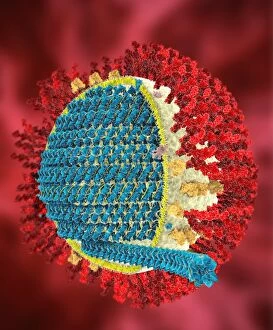
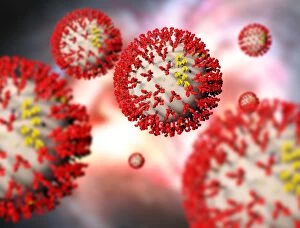
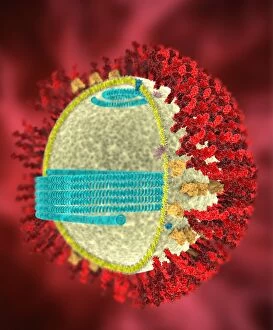
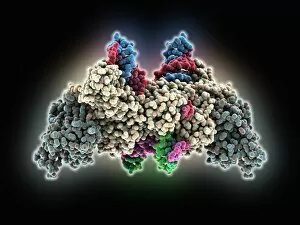
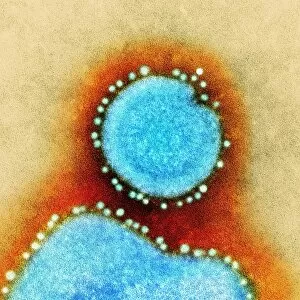
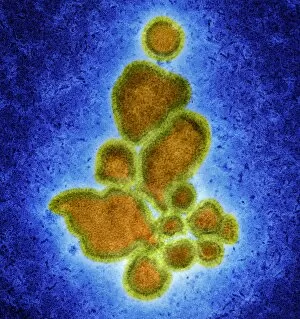
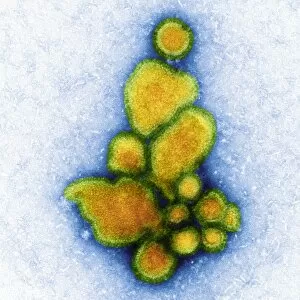
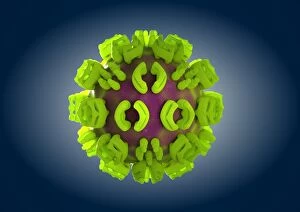
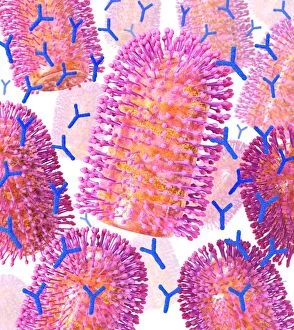
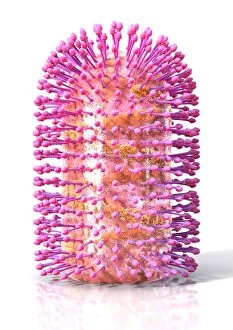
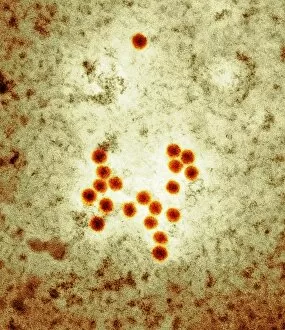
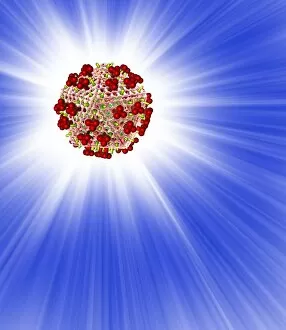
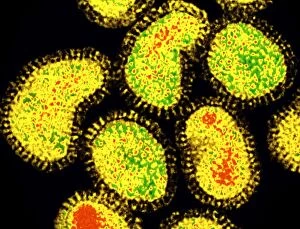
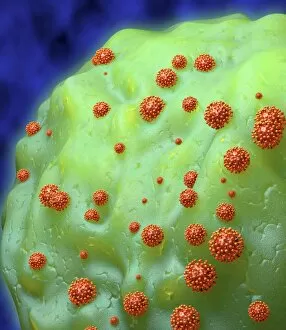
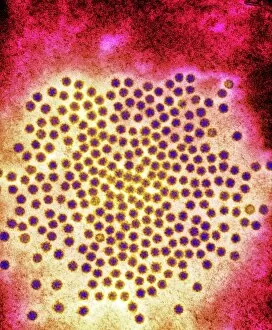
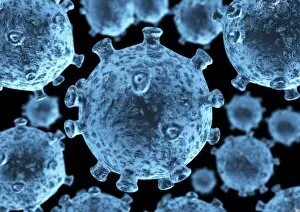
RNA viruses are a diverse group of infectious agents that have captured the attention of scientists and researchers worldwide. From the intricate structure of HIV particles to the menacing Norovirus particles observed under a transmission electron microscope (TEM), these tiny entities hold immense significance in our understanding of viral diseases. Influenza, one of the most well-known RNA viruses, has been depicted through computer artwork, showcasing its complex architecture and highlighting its ability to mutate rapidly. TEM images further reveal the true face of influenza virus particles, resembling miniature spheres with spikes protruding from their surface. Hepatitis C viruses also fall into this category, as revealed by TEM imaging. These minute structures can wreak havoc on liver cells and cause chronic infections if left untreated. The artistic representation of rotavirus particle emphasizes its distinctive wheel-like shape, which is responsible for causing severe diarrhea in young children. Molecular models depicting rhinovirus alongside antibodies shed light on potential therapeutic strategies against common colds caused by this RNA virus. Similarly, an SEM image showcases an HIV-infected macrophage - a key player in spreading this deadly virus throughout the body. The captivating artwork capturing infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) highlights how RNA viruses can affect not only humans but also animals like poultry. L-A virus and Coxsackievirus are two more examples that demonstrate the wide range of hosts susceptible to RNA viral infections. As we delve deeper into studying these enigmatic entities known as RNA viruses, we uncover their remarkable adaptability and ability to exploit host cells for replication. Understanding their mechanisms will undoubtedly pave the way for novel treatments and preventive measures against these relentless adversaries that continue to challenge human health globally.