Secretory Cell Collection
The secretory cell, a microscopic wonder hidden within our bodies, plays a crucial role in various organs and systems
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
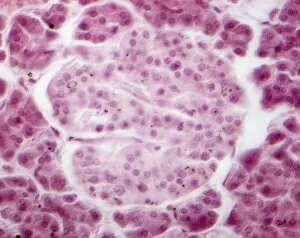
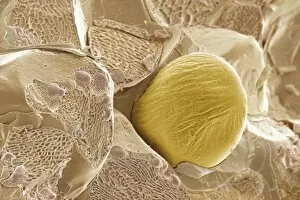
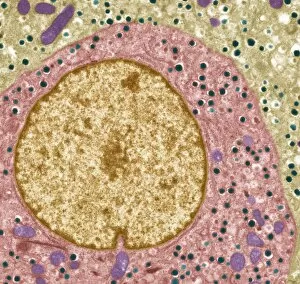
The secretory cell, a microscopic wonder hidden within our bodies, plays a crucial role in various organs and systems. Let's embark on a journey through the intricate world of these fascinating cells. In the Islet of Langerhans, we find secretory cells working tirelessly to regulate blood sugar levels. Under the lens of a light micrograph, their distinct arrangement becomes apparent, forming clusters amidst surrounding tissues. Moving on to another realm of secrets revealed by science, we encounter an enchanting image captured by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Here lies ginger - not just a spice but also home to secretory cells that contribute to its unique flavor profile. Delving deeper into the mysteries concealed within our reproductive system, we stumble upon an astonishing false-color SEM image showcasing spermatozoa clinging onto the uterine wall. These secretive cells navigate their way towards fertilization with remarkable precision. Shifting gears towards the pituitary gland, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) unravels its hidden secrets. The TEM images expose intricately structured secretory cells bustling with activity as they release vital hormones essential for bodily functions. Venturing further into this captivating labyrinth of secrets guarded by nature itself, SEM unveils yet another revelation: the internal wall of the uterus adorned with specialized secretory cells. Their presence hints at their pivotal role in creating an optimal environment for nurturing life. Goblet cells emerge from obscurity as SEM captures their distinctive shape and function within our respiratory and digestive tracts. These mucus-secreting heroes protect delicate tissues from harm while ensuring smooth passage for air or food. Returning to pancreatic territory through SEM imagery reveals acini cells nestled together like puzzle pieces. These exocrine glands secrete enzymes necessary for digestion and are instrumental in maintaining overall gut health. As we bid farewell to this expedition into secrecy held by cellular wonders, let us not forget one final destination – Fallopian tubes – where countless enigmatic secretory cells await further exploration.