Si Unit Collection
"Unveiling the Legacy of SI Unit
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
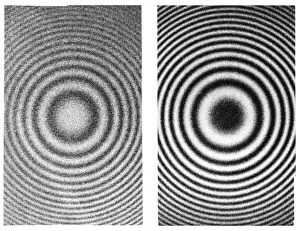
"Unveiling the Legacy of SI Unit: A Journey through the Minds of Visionaries" Step into the world of scientific pioneers as we explore the fascinating history behind the SI unit. One such luminary is Nikola Tesla, a Serb-US physicist whose groundbreaking work revolutionized our understanding of electricity and magnetism. In this captivating journey, we encounter remarkable inventions like the Kelvin thermometer, an ingenious device that measures temperature with unparalleled accuracy. Marvel at artwork C017 / 3608, which beautifully captures the essence of this remarkable instrument. Delving deeper into precision measurement, we discover the Primary Standard Radiation Force Balance C016 / 6478 - a true marvel in its ability to accurately quantify radiation forces. Its counterparts, C016 / 6479 and C016 / 6477, further exemplify humanity's quest for precise standards. The contributions continue as we learn about Wilhelm Weber, a German physicist who paved the way for modern electrical measurements. Witness awe-inspiring interference rings as length standards (C016 / 2056) that showcase Weber's ingenuity in establishing reliable benchmarks. Bank of Weston cells (C016 / 2041) and Ayrton-Jones ampere balance (C016 / 2034) take center stage next – two extraordinary creations instrumental in defining electrical units with utmost precision. These innovations demonstrate how meticulous engineering has shaped our understanding of fundamental quantities. Returning to Tesla's brilliance, his caricature (C015/6713) reminds us not only of his immense contributions but also his unique persona that captivated generations worldwide. Finally, let us pay homage to Werner Siemens – a German engineer whose name echoes throughout scientific circles even today. His pioneering efforts have left an indelible mark on metrology and engineering alike; truly a testament to human ingenuity. As we conclude this enlightening journey through time and innovation surrounding SI units' development, may it inspire future generations to push boundaries and unravel the mysteries of our universe.