Star Death Collection (#3)
"Exploring the Cosmic Spectacle: Unveiling the Mysteries of Star Death" Witness the mesmerizing beauty of the Crab Nebula (M1
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
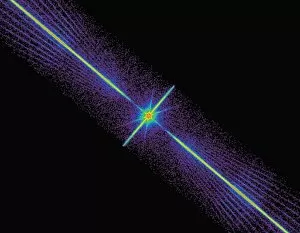
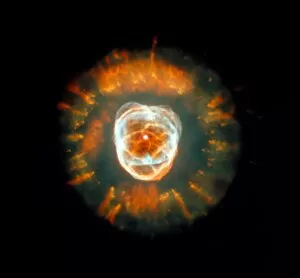
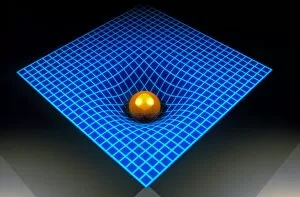
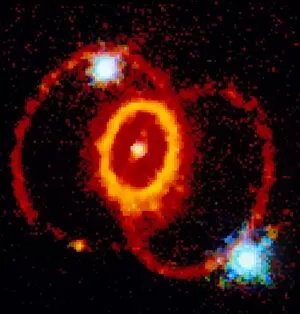
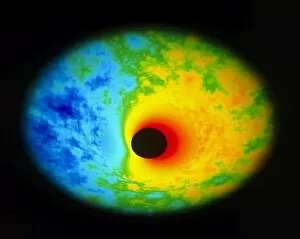
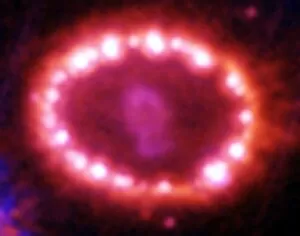
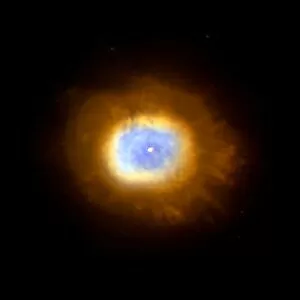
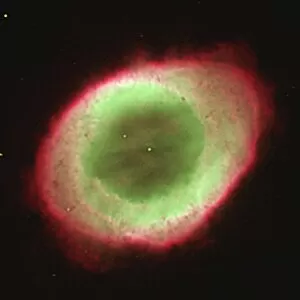
"Exploring the Cosmic Spectacle: Unveiling the Mysteries of Star Death" Witness the mesmerizing beauty of the Crab Nebula (M1), a celestial masterpiece born from a supernova explosion that occurred in 1054 AD. Behold this captivating composite image of the Crab Nebula, showcasing its intricate details and vibrant colors, revealing nature's artistic prowess. Through breathtaking artwork, delve into the cataclysmic event known as a supernova explosion, where stars bid their final farewell in an awe-inspiring display of energy release. Experience ethereal light echoes reverberating through space, remnants of an exploding star that continue to captivate astronomers' imagination and unravel cosmic secrets. Marvel at a distant galaxy's stellar demise as it unleashes a dazzling supernova spectacle, illuminating vast regions with its radiant glow before fading into obscurity. Gaze upon planetary nebulae – celestial cocoons formed by dying stars – as they paint the cosmos with their vivid hues and intricate structures like brushstrokes on an interstellar canvas. Delve deeper into cosmic wonders with Spitzer's infrared lens capturing the Helix Nebula's hidden beauty - unveiling layers unseen by human eyes but cherished by stargazers worldwide. Immerse yourself in Hubble Space Telescope's iconic image of the Helix Nebula; witness its delicate tendrils stretching across space like wisps of celestial smoke frozen in time. Encounter red dwarf stars - long-lived yet destined for ultimate decay - silently burning out while leaving behind enigmatic traces that intrigue scientists seeking answers about our universe's fate. Venture towards mysterious black holes lurking within cosmic depths; these enigmatic gravitational monsters devour matter relentlessly while shaping galaxies around them. Explore another facet of Helix Nebula’s splendor—a planetary nebula—unfolding before your eyes like a cosmic butterfly, showcasing the grandeur of stellar evolution.