Subunits Collection
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Subunits: From Cholera Toxin to Photosystem I" Exploring the Molecular World
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
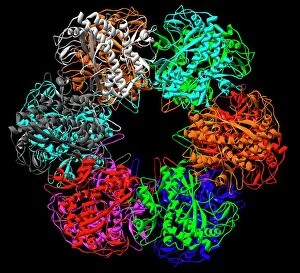
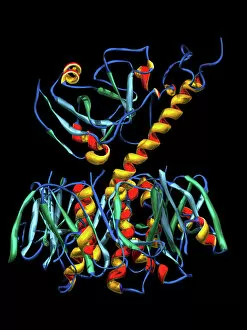
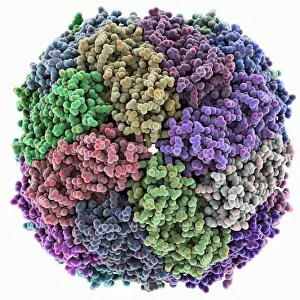
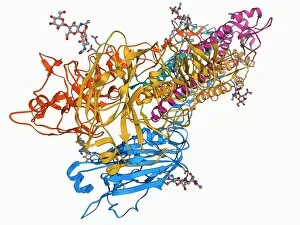
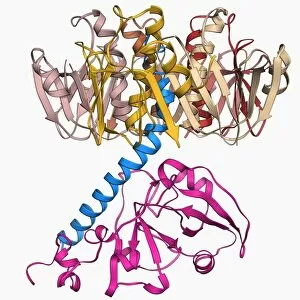
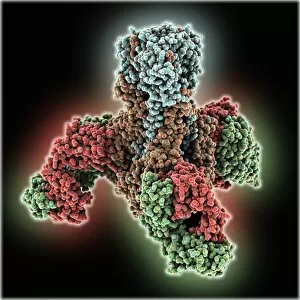
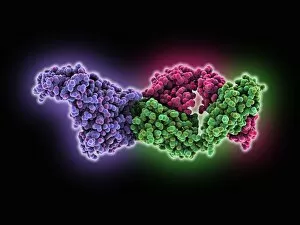
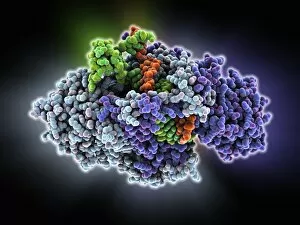
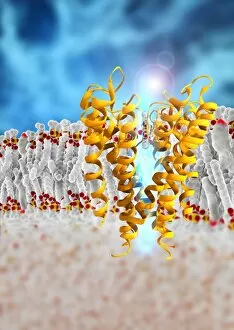
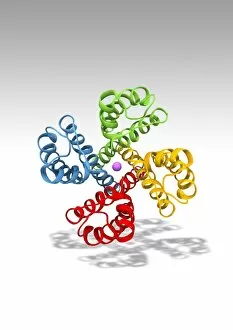
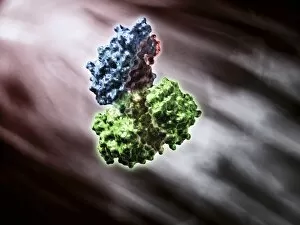
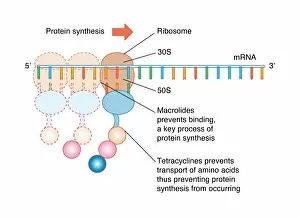
"Unveiling the Intricacies of Subunits: From Cholera Toxin to Photosystem I" Exploring the Molecular World: A glimpse into subunits like Cholera toxin and Glutamine synthetase enzyme through their intricate molecular models. Iron's Crucial Role: Unraveling the significance of iron-containing proteins as we delve into their mesmerizing molecular structures. H5N1 Haemagglutinin Protein Subunit F006 / 9590: Understanding the building blocks of this vital protein subunit, paving the way for potential breakthroughs in combating influenza viruses. Decoding Cholera Toxin Molecule F006 / 9546: Delving into the complexities of cholera toxin at a microscopic level, offering insights for improved treatments against this infectious disease. Transducin Protein Beta-Gamma Complex F006 / 9514: Peering into the intricacies of this complex subunit, shedding light on its role in signal transduction pathways within our cells. Haemagglutinin Protein Subunit F006 / 9479: Unmasking the secrets behind this crucial protein subunit that plays a pivotal role in viral entry and infection mechanisms. Haemagglutinin Viral Surface Protein F006 / 9470: Examining how this surface protein aids viruses in binding to host cells, providing valuable knowledge for antiviral strategies. Illuminating Photosystem I Molecule F006 / 9380: Discovering nature's energy conversion process through exploring photosystem I's captivating molecular structure. The Power Duo - Transducin Protein Beta-Gamma Complexes (F006/9514): Diving deeper into these dynamic duos that regulate cellular responses and contribute to various physiological functions within our bodies. Unveiling Haemagglutinin Viral Surface Protein C015 / 9965.