Thrombocyte Collection
Thrombocytes, also known as platelets, play a crucial role in our blood clotting process
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
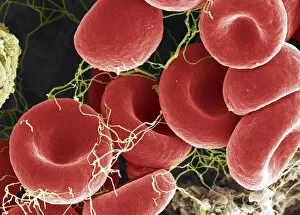
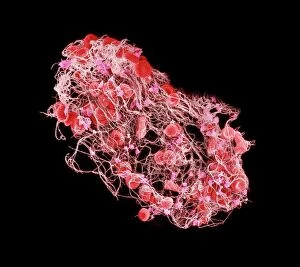
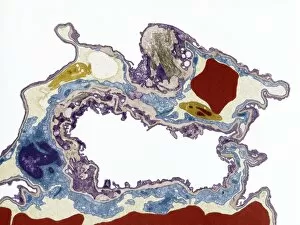
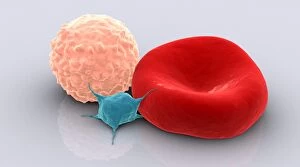
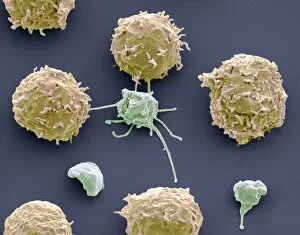
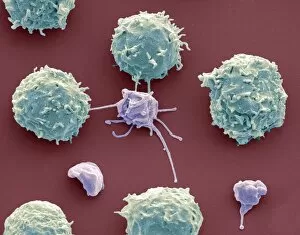
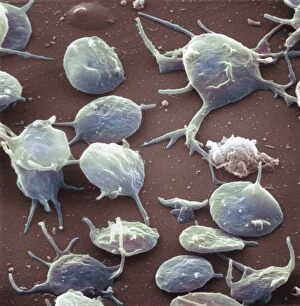
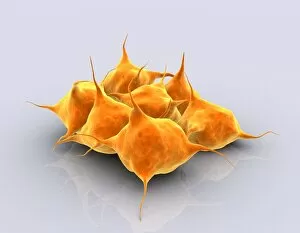
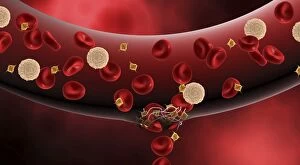
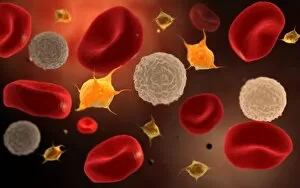
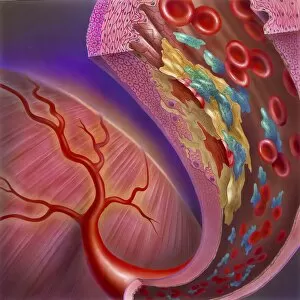
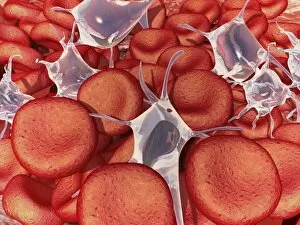
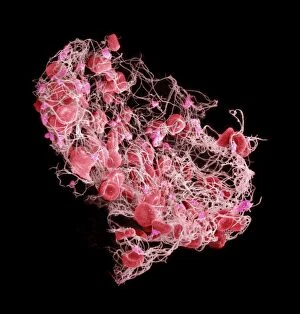
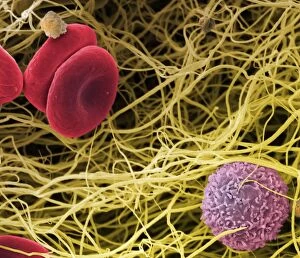
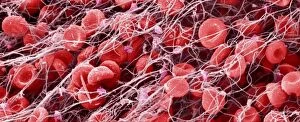
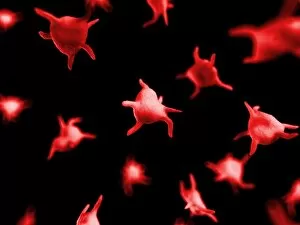
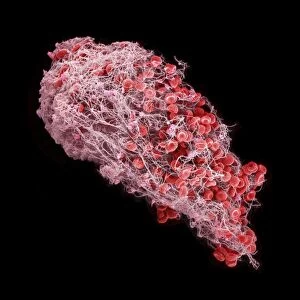
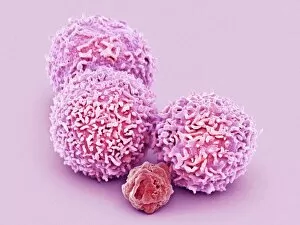
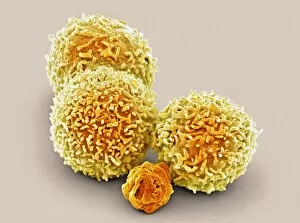
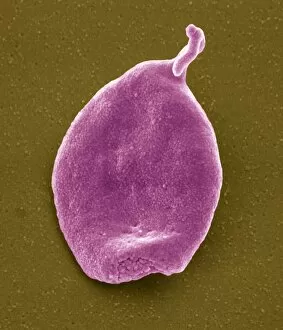
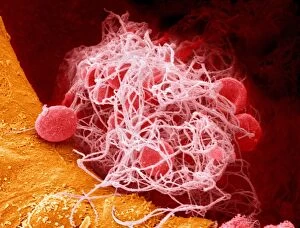
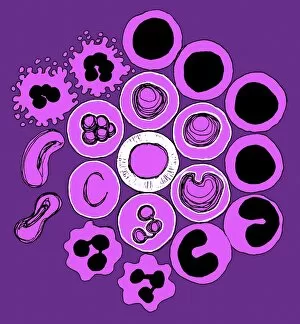
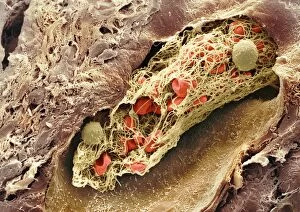
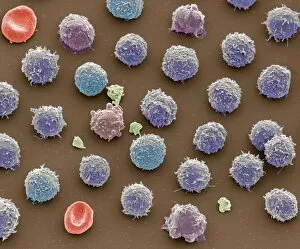
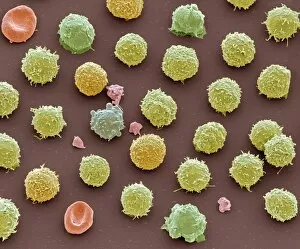
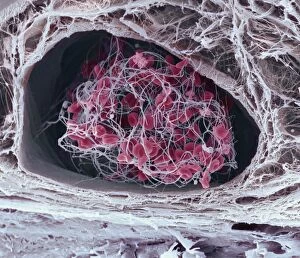
Thrombocytes, also known as platelets, play a crucial role in our blood clotting process. These tiny cell fragments are captured beautifully under the scanning electron microscope (SEM C016 / 9747), showcasing their intricate structure. In this conceptual image, we witness the collaboration between thrombocytes and other blood components like red and white blood cells. It's fascinating to see how these different elements work together to form a protective barrier against bleeding or injury (Platelets, SEM). Another captivating artwork (Blood clot, artwork C016 / 4619) depicts the formation of a blood clot. This natural defense mechanism prevents excessive bleeding by forming a mesh-like structure composed of platelets and fibrin strands. Under SEM observation (White blood cells and platelets, SEM C016 / 3099), we can appreciate the unique characteristics of both white blood cells and platelets. Their distinct shapes and sizes contribute to their specific functions within our immune system. A conceptual image featuring platelets alongside red blood cells highlights their close association during normal physiological processes (Conceptual image of platelets with red blood cells). Moreover, another conceptual image showcases an assembly of these remarkable cell fragments called "a group of platelets, " emphasizing their collective power in maintaining hemostasis. When examining a cross-section of an artery, we can observe the stark contrast between a healthy vessel and one affected by plaque buildup or thrombus formation (Normal artery compared to plaque and thrombus formation in artery). Thrombocytes play an essential role in preventing such complications by swiftly responding to injuries within our circulatory system. These captivating images shed light on the intricate world of thrombocytes – from their microscopic structures seen through powerful microscopes to their vital contributions in safeguarding our health.