Tibial Collection
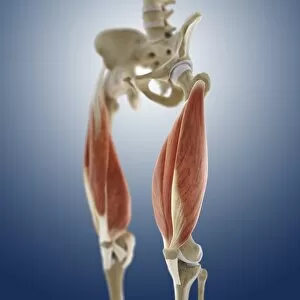
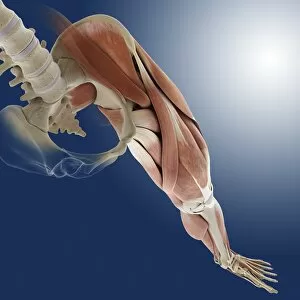
The tibial bone plays a crucial role in the stability and movement of our lower limbs
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
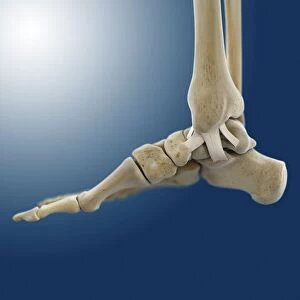
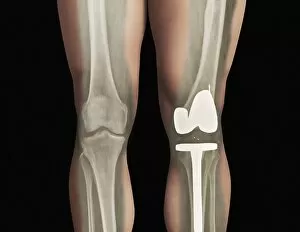
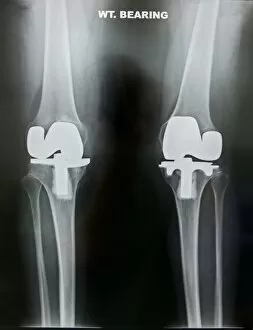
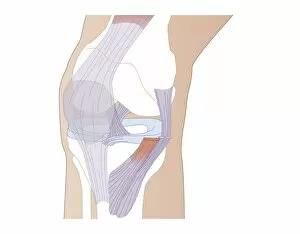
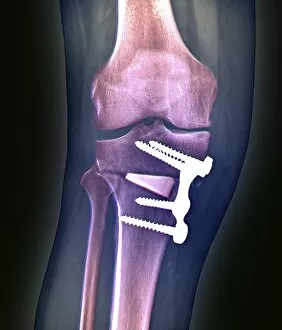
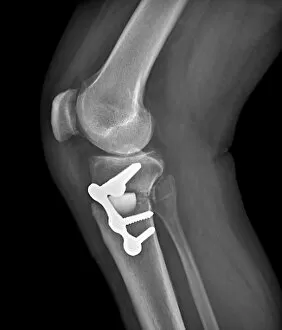
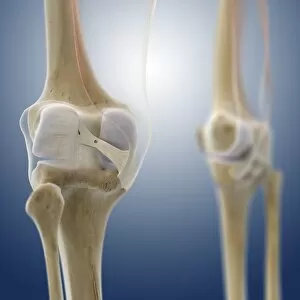
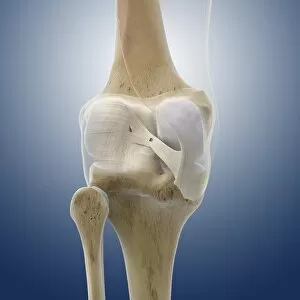
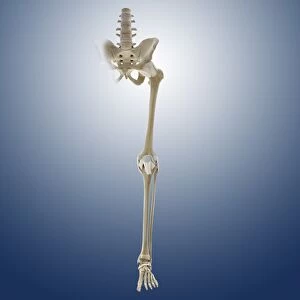
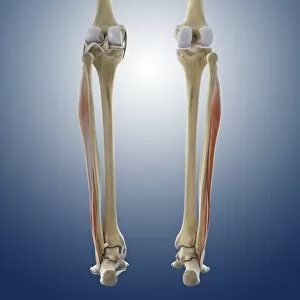
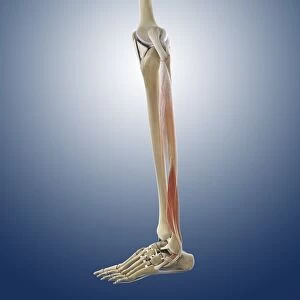
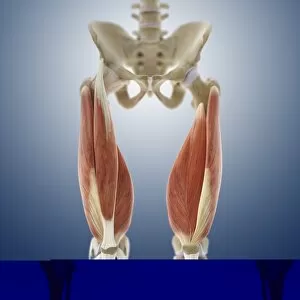
The tibial bone plays a crucial role in the stability and movement of our lower limbs. Located on the inner side of the leg, it is connected to various ligaments that provide support and strength. One such set of ligaments are the inner ankle ligaments, which work in harmony with the tibial bone to maintain balance and prevent excessive inward rolling of the foot during activities. In medical artwork C013 / 4451, we can see a detailed representation of these inner ankle ligaments, highlighting their intricate structure and importance in maintaining joint integrity. Moving up from the ankle, we come across another significant aspect related to the tibia - total knee replacement. X-ray images reveal how this surgical procedure involves replacing damaged knee joints with artificial ones, providing relief for individuals suffering from severe arthritis or injury. Obesity can pose challenges when it comes to artificial knee joints. X-ray images demonstrate how excess weight places additional stress on these prosthetics. However, advancements in medical technology continue to improve outcomes for patients even in such cases. Knee ligaments also rely on the tibia for support and function. Artwork depicting these structures showcases their interplay with other components within our knees, ensuring stability during movements like walking or running. For those requiring realignment surgery due to misalignment or deformities affecting their knees' functionality, X-rays offer valuable insights into pre-operative assessments as well as post-operative progress monitoring. Images labeled C016 / 6604 through C016 / 6599 display different stages of knee realignment surgeries performed on patients using advanced imaging techniques. Additionally, artwork labeled C013 / 4662 focuses specifically on knee ligament anatomy while emphasizing their significance in maintaining joint stability throughout various activities. Lastly, let's not forget about collateral knee ligaments that contribute significantly to overall knee stability. Artwork dedicated solely to illustrating these structures helps us understand their location and function better within our legs' complex network of ligaments.