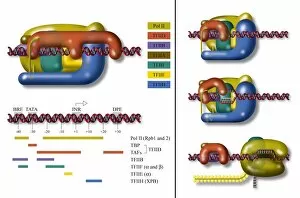
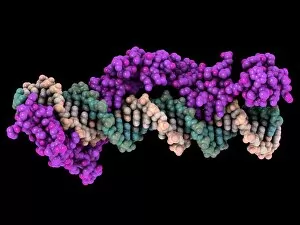
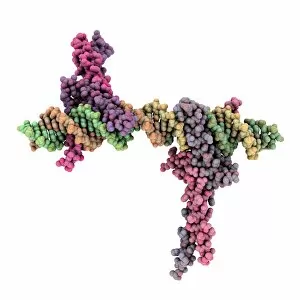
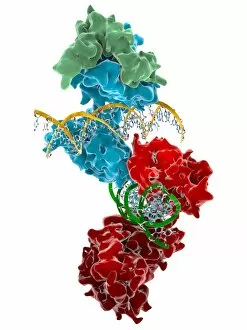
Transcription Factor Collection (#2)
A transcription factor is a crucial player in the intricate process of gene expression
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
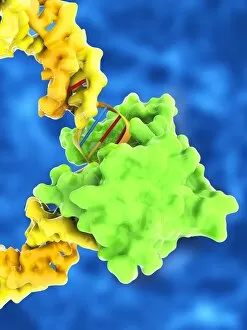
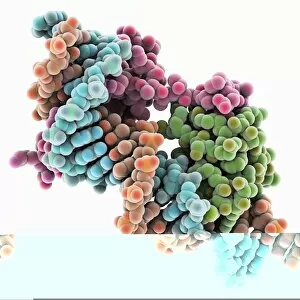
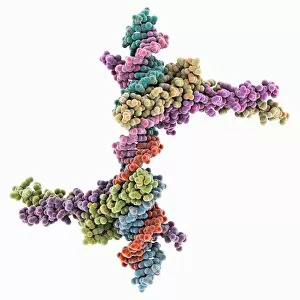
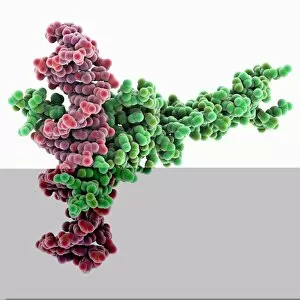
A transcription factor is a crucial player in the intricate process of gene expression. One such example is the MyoD muscle protein-DNA complex, which plays a pivotal role in regulating muscle development and differentiation. Another important transcription factor complex is the TATA box-binding protein (TBP) complex C017 / 7082. This specific complex binds to the TATA box sequence on DNA, initiating transcription by recruiting other factors necessary for RNA synthesis. In addition to its involvement in gene regulation, the TBP complex C017 / 7088 also interacts with various other complexes like C017 / 7084 and C014 / 0867. These interactions further enhance its ability to initiate transcription at specific sites on DNA. Furthermore, another significant interaction involves a transcription factor bound to ribosomal RNA, highlighting its role in controlling protein synthesis within cells. This demonstrates how these factors are not limited to regulating gene expression alone but also have an impact on essential cellular processes. The Pho4 transcription factor bound to DNA (C014 / 0861) showcases yet another fascinating aspect of these proteins' functionality. By binding specifically to certain regions of DNA, this particular factor regulates phosphate metabolism genes, ensuring proper nutrient utilization within cells.