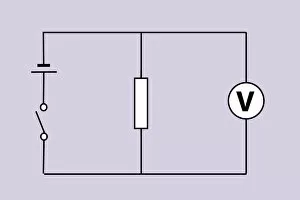
Voltage Collection (#2)
"Voltage: Illuminating the Power of Electricity" Step into the enchanting world of Variety Theatre, where Dr
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
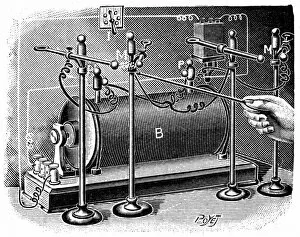
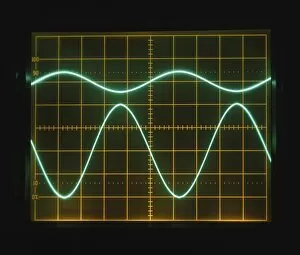
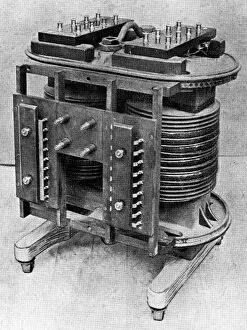
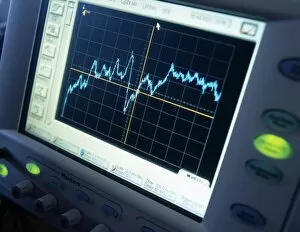
"Voltage: Illuminating the Power of Electricity" Step into the enchanting world of Variety Theatre, where Dr. Walford Bodie astounds audiences with his electrifying performances. With a flicker and a spark, he mesmerizes all with the wonders of voltage. At the heart of this captivating spectacle lies an electricity substation, buzzing with energy as it powers not only the theater but also our modern lives. From a fruit-powered clock to solar panels basking in the sun's rays, voltage is harnessed in various forms to bring light and life to our world. Delve deeper into this electric realm and you'll encounter Campbell's standard of mutual inductance, meticulously measured by an oscilloscope. Ceramic insulators stand tall, protecting us from high voltage AC transmission pylons that connect distant places through invisible currents. But let us not forget the roots of this powerful force – The Voltaic pile (battery). Drawing inspiration from Alessandro Volta's letter, we witness how his invention brought forth a new era in electrical science. A voltaic pile crafted for Jacques Alexandre Charles serves as a testament to their pioneering spirit. Voltage holds within it both mystery and potential; it fuels our homes, propels innovation forward, and lights up our nights. So next time you flip on a switch or charge your devices, take a moment to appreciate the incredible power behind that simple act – Voltage: illuminating possibilities beyond imagination.