Wind Pipe Collection (#3)
The windpipe, also known as the trachea, plays a vital role in our respiratory system. It serves as a pathway for air to travel from the nose and mouth into the lungs
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
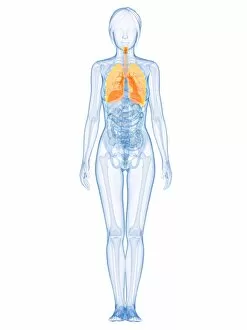
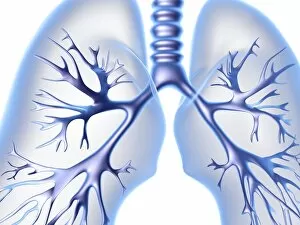
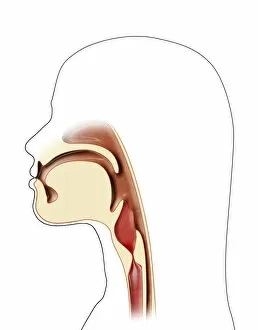
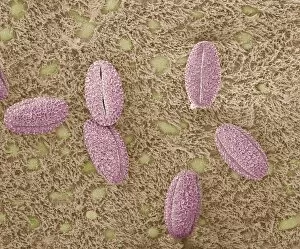
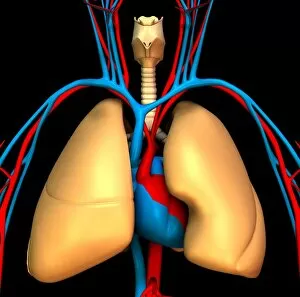
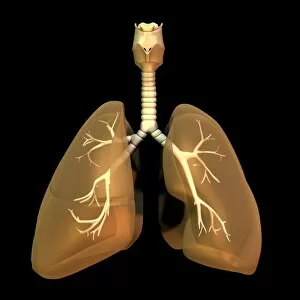
The windpipe, also known as the trachea, plays a vital role in our respiratory system. It serves as a pathway for air to travel from the nose and mouth into the lungs. To understand its function better, let's take a closer look at its structure. A diagram of the lungs and bronchial tubes reveals how the windpipe connects directly to these essential organs. This connection allows oxygen to be transported efficiently throughout our body. Another informative diagram showcases not only the heart and lungs but also highlights the presence of this crucial tube called the windpipe. Its location is key in ensuring that oxygenated blood reaches every part of our body. Moving on to anatomy, we explore the muscles of the neck which surround and support this vital organ. These muscles aid in maintaining proper posture while protecting and stabilizing our windpipe. Examining it under scanning electron microscopy (SEM), we can observe intricate details of its lining - an impressive network designed to filter out impurities present inhaled air may carry with it. The larynx or voice box is another fascinating aspect related to our topic at hand –the windpipe. Artwork depicting this structure helps us visualize how it functions during speech production while still allowing air passage through. Human lungs are incomplete without mentioning their direct connection with this indispensable tube -the trachea. Their interdependence ensures efficient gas exchange within our bodies, enabling us to breathe effortlessly. Further SEM images provide microscopic views of tracheal linings revealing cilia-covered surfaces that help trap foreign particles before they reach sensitive lung tissues – an incredible defense mechanism. Allergens can pose challenges when they enter our respiratory system; however, understanding their presence within such important structures like trachea aids researchers in developing effective treatments for allergies caused by airborne substances. A captivating SEM image solely focusing on just this remarkable tube itself gives us a glimpse into its complexity and beauty simultaneously highlighting its significance within human anatomy.