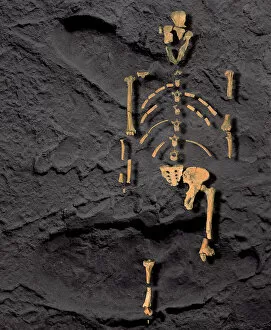Anthropology Collection
"Unveiling the Tapestry of Human History
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
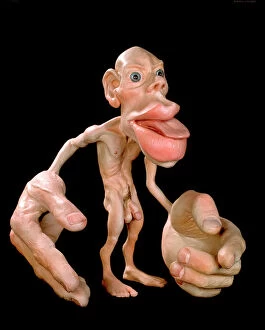
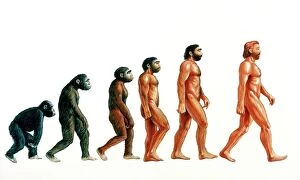
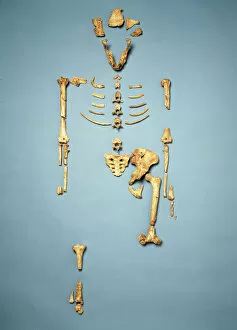
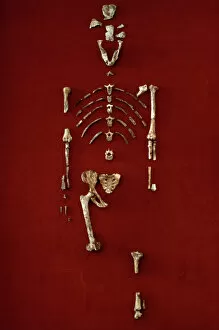
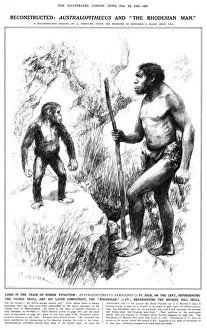
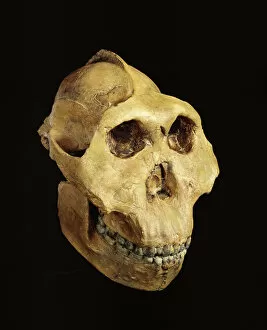
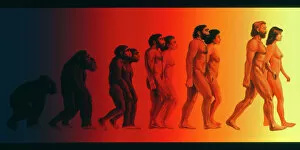
"Unveiling the Tapestry of Human History: Exploring Anthropology through Time and Space" Embark on a captivating journey into the depths of human existence as we delve into anthropology, the study of our species' origins, development, and cultural diversity. From ancient cave paintings to fossil footprints, each artifact serves as a portal connecting us to our ancestors and shedding light on their lives. Step back in time with the Lascaux II cave painting replica C013/7378. Marvel at the intricate details etched by Stone-Age artists in Chauvet, France, transporting you to an era long gone. These vivid depictions offer glimpses into early human societies and their connection to nature. Venture further across continents to Argentina's Cave of the Hands—a mesmerizing display of prehistoric artistry. The handprints adorning its walls serve as a testament to humanity's desire for self-expression throughout history. It also unveils our physical evolution through hominid crania like Australopithecus afarensis (AL 288-1), affectionately known as Lucy. These fossilized remains provide invaluable insights into our ancestral lineage and shed light on how we evolved over millions of years. Follow in the footsteps—quite literally—of early humans along the Trail of Laetoli footprints. Preserved for eternity in volcanic ash, these imprints offer tangible evidence of bipedal locomotion among our distant relatives. As we explore anthropology's intricacies, we encounter not only artistic expressions but also scientific discoveries such as motor homunculus—an illustration mapping sensory perception onto specific brain regions. This revelation deepens our understanding of how humans interact with their surroundings. Delving deeper still reveals stages in human evolution that shaped who we are today—the gradual progression from primitive tools like prehistoric spear-throwers to complex civilizations that have flourished throughout time.