Biochemistry Collection (#6)
Biochemistry is the fascinating study of the chemical processes and substances that occur within living organisms
For sale as Licensed Images
Choose your image, Select your licence and Download the media
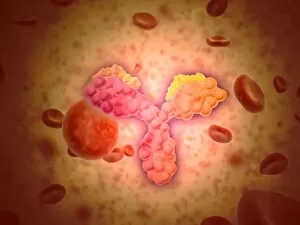
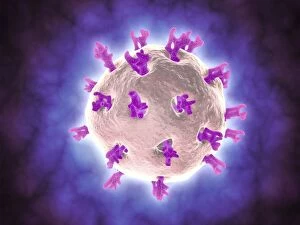
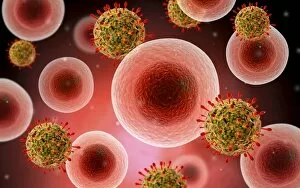
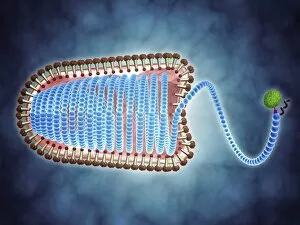
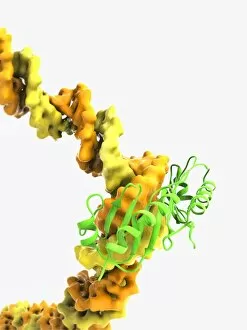
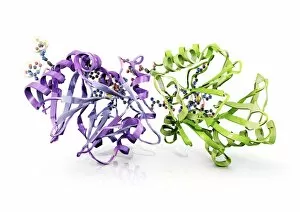
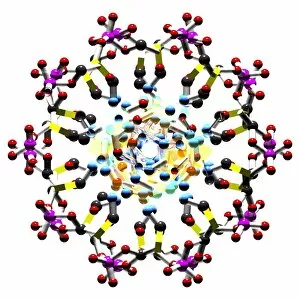
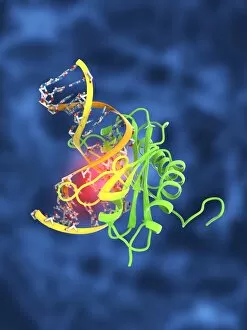
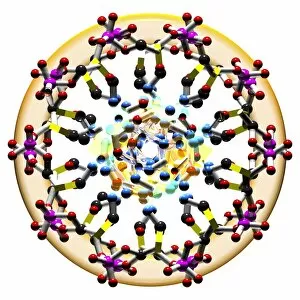
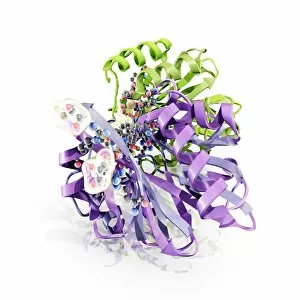
Biochemistry is the fascinating study of the chemical processes and substances that occur within living organisms. In this captivating field, scientists delve into the intricate mechanisms that govern life itself. One intriguing aspect involves anaesthetics inhibiting an ion channel (C015 / 6718), revealing how these compounds can block nerve signals and induce temporary loss of sensation. Another captivating image showcases the structure of an Immunoglobulin G antibody molecule, highlighting its crucial role in our immune system's defense against pathogens. In a mesmerizing light micrograph, EDTA crystals are captured in all their splendor, showcasing their unique geometric patterns. Similarly, another image displays Immunoglobulin G antibody molecules (F007 / 9894) with astonishing detail, emphasizing their ability to recognize and neutralize foreign invaders. The beauty extends beyond static images; it also encompasses dynamic processes. A stunning artwork depicts the cell membrane (C013 / 7467), illustrating its vital function as a barrier and gatekeeper for essential molecules entering or leaving cells. Exploring further into our body's inner workings, we encounter a captivating artwork depicting the blood coagulation cascade (C016 / 9873). This complex series of reactions ensures proper clotting when injuries occur to prevent excessive bleeding. DNA takes center stage in another illustration, showcasing its double helix structure that carries genetic information responsible for traits passed down from generation to generation. Additionally, a microscopic view reveals human respiratory syncytial virus—a reminder of both the beauty and danger found at microscopic levels. Delving deeper into molecular interactions, we witness zinc fingers bound to a DNA strand—an elegant representation of how proteins regulate gene expression by binding specific sequences on DNA molecules. It also sheds light on hormones' crystalline forms—oxytocin hormone crystals (PLM C016 / 7196) demonstrate this phenomenon beautifully while testosterone crystals captivate us under polarized light microscopy (PLM).